When the clock ticks wrong with COVID-19
- PMID: 36394205
- PMCID: PMC9670202
- DOI: 10.1002/ctm2.949
When the clock ticks wrong with COVID-19
Abstract
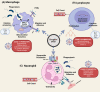
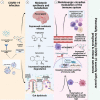
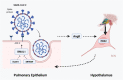
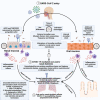
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) is a member of the coronavirus family that causes the novel coronavirus disease first diagnosed in 2019 (COVID-19). Although many studies have been carried out in recent months to determine why the disease clinical presentations and outcomes can vary significantly from asymptomatic to severe or lethal, the underlying mechanisms are not fully understood. It is likely that unique individual characteristics can strongly influence the broad disease variability; thus, tailored diagnostic and therapeutic approaches are needed to improve clinical outcomes. The circadian clock is a critical regulatory mechanism orchestrating major physiological and pathological processes. It is generally accepted that more than half of the cell-specific genes in any given organ are under circadian control. Although it is known that a specific role of the circadian clock is to coordinate the immune system's steady-state function and response to infectious threats, the links between the circadian clock and SARS-CoV-2 infection are only now emerging. How inter-individual variability of the circadian profile and its dysregulation may play a role in the differences noted in the COVID-19-related disease presentations, and outcome remains largely underinvestigated. This review summarizes the current evidence on the potential links between circadian clock dysregulation and SARS-CoV-2 infection susceptibility, disease presentation and progression, and clinical outcomes. Further research in this area may contribute towards novel circadian-centred prognostic, diagnostic and therapeutic approaches for COVID-19 in the era of precision health.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2 infection; circadian clock; clinical outcomes; epigenetics; microRNAs; oral and systemic precision health; personalized medicine.
© 2022 The Authors. Clinical and Translational Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Shanghai Institute of Clinical Bioinformatics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Dong Y, Mo X, Hu Y, et al. Epidemiology of COVID‐19 among children in China. Pediatrics. 2020;145:e20200702. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
