APOE ε4 carrier status and sex differentiate rates of cognitive decline in early- and late-onset Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 36394443
- PMCID: PMC10182251
- DOI: 10.1002/alz.12831
APOE ε4 carrier status and sex differentiate rates of cognitive decline in early- and late-onset Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
Background: We studied the effect of apolipoprotein E (APOE) ε4 status and sex on rates of cognitive decline in early- (EO) and late- (LO) onset Alzheimer's disease (AD).
Method: We ran mixed-effects models with longitudinal cognitive measures as dependent variables, and sex, APOE ε4 carrier status, and interaction terms as predictor variables in 998 EOAD and 2562 LOAD participants from the National Alzheimer's Coordinating Center.
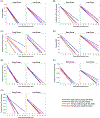
Results: APOE ε4 carriers showed accelerated cognitive decline relative to non-carriers in both EOAD and LOAD, although the patterns of specific cognitive domains that were affected differed. Female participants showed accelerated cognitive decline relative to male participants in EOAD only. The effect of APOE ε4 was greater in EOAD for executive functioning (p < 0.0001) and greater in LOAD for language (p < 0.0001).
Conclusion: We found APOE ε4 effects on cognitive decline in both EOAD and LOAD and female sex in EOAD only. The specific patterns and magnitude of decline are distinct between the two disease variants.
Highlights: Apolipoprotein E (APOE) ε4 carrier status and sex differentiate rates of cognitive decline in early-onset (EO) and late-onset (LO) Alzheimer's disease (AD). APOE ε4 in EOAD accelerated decline in memory, executive, and processing speed domains. Female sex in EOAD accelerated decline in language, memory, and global cognition. The effect of APOE ε4 was stronger for language in LOAD and for executive function in EOAD. Sex effects on language and executive function decline differed between EOAD and LOAD.
Keywords: APOE ε4; cognitive decline; early-onset Alzheimer's disease; late-onset Alzheimer's disease; sex differences.
© 2022 the Alzheimer's Association.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
Declaration of interest for A.J.P., P.E.L, K.A.L, M.K.M., S.N., A.B.S., and S.G.: none. L.G.A. has received personal compensation in the range of $500 to $4999 for serving as a Consultant for National Institutes of Health (NIH), Florida Dept of Health, NIH Biobank, Eli Lilly, and GE Healthcare. L.G.A. has received personal compensation in the range of $500 to $4999 for serving on a Scientific Advisory or Data Safety Monitoring board for Eisai and serving on a Scientific Advisory or Data Safety Monitoring board for Two Labs. L.G.A. has received personal compensation in the range of $5000 to $9999 for serving as a Consultant for Biogen, serving on a Scientific Advisory or Data Safety Monitoring board for IQVIA, and serving on a Scientific Advisory or Data Safety Monitoring board for Biogen. L.G.A. has received personal compensation in the range of $10,000 to $49,999 for serving as an Editor, Associate Editor, or Editorial Advisory Board Member for the Alzheimer’s Association. An immediate family member of L.G.A. has stock in Semiring, Cassava Neurosciences, and Golden Seed. The institution of L.G.A. has received research support from Roche, National Institute on Aging (NIA), Alzheimer’s Association, AVID radiopharmaceuticals, and Life Molecular Imaging. Author disclosures are available in the supporting information.
Figures

References
-
- Koedam ELGE, Lauffer V, Van Der Vlies AE, Van Der Flier WM, Scheltens P, Pijnenburg YAL. Early-versus late-onset Alzheimer’s disease: more than age alone. J Alzheimers Dis. 2010;19(4):1401–1408. - PubMed
-
- Van Der Vlies AE, Koedam ELGE, Pijnenburg YAL, Twisk JWR, Scheltens P, Van Der Flier WM. Most rapid cognitive decline in APOE epsilon4 negative Alzheimer’s disease with early onset. Psychol Med. 2009;39(11):1907–1911. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P50 AG005142/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG016573/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG047266/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG010161/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG025688/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005133/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P20 AG068077/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG072977/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG033514/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG013854/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG053760/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P20 AG068082/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG010124/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG023501/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P20 AG068053/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005131/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG010133/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG057195/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG016574/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005146/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 AG072122/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG035982/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG008702/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG016976/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG008051/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005681/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG013846/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG047270/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005136/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG049638/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG012300/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005134/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG008017/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066546/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005138/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG047366/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P20 AG068024/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG072958/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG072976/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG010129/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG019610/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG072947/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG072959/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG028383/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

