Molecular source attribution
- PMID: 36395093
- PMCID: PMC9671344
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1010649
Molecular source attribution
Conflict of interest statement
We have no competing interests to declare.
Figures

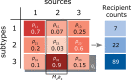
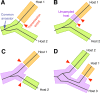

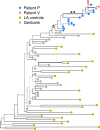
Similar articles
-
A combined case-control and molecular source attribution study of human Campylobacter infections in Germany, 2011-2014.Sci Rep. 2017 Jul 11;7(1):5139. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-05227-x. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28698561 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Identification of Host-Segregating Single-Nucleotide Polymorphisms for Source Attribution of Clinical Campylobacter coli Isolates.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2020 Nov 24;86(24):e01787-20. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01787-20. Print 2020 Nov 24. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 33036986 Free PMC article.
-
Bayesian temporal source attribution of foodborne zoonoses: Campylobacter in Finland and Norway.Risk Anal. 2011 Jul;31(7):1156-71. doi: 10.1111/j.1539-6924.2010.01558.x. Epub 2011 Jan 13. Risk Anal. 2011. PMID: 21231942
-
Salmonella source attribution based on microbial subtyping.Int J Food Microbiol. 2013 May 15;163(2-3):193-203. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2013.03.005. Epub 2013 Mar 16. Int J Food Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23562696 Review.
-
Vaccination of chickens against Campylobacter.Vaccine. 2007 Jul 26;25(30):5548-57. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2006.12.002. Epub 2006 Dec 15. Vaccine. 2007. PMID: 17224215 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

