Enoxaparin for outpatients with COVID-19: 90-day results from the randomised, open-label, parallel-group, multinational, phase III OVID trial
- PMID: 36396519
- PMCID: PMC9657896
- DOI: 10.1016/j.thromres.2022.10.021
Enoxaparin for outpatients with COVID-19: 90-day results from the randomised, open-label, parallel-group, multinational, phase III OVID trial
Abstract
Introduction: The benefits of early thromboprophylaxis in symptomatic COVID-19 outpatients remain unclear. We present the 90-day results from the randomised, open-label, parallel-group, investigator-initiated, multinational OVID phase III trial.
Methods: Outpatients aged 50 years or older with acute symptomatic COVID-19 were randomised to receive enoxaparin 40 mg for 14 days once daily vs. standard of care (no thromboprophylaxis). The primary outcome was the composite of untoward hospitalisation and all-cause death within 30 days from randomisation. Secondary outcomes included arterial and venous major cardiovascular events, as well as the primary outcome within 90 days from randomisation. The study was prematurely terminated based on statistical criteria after the predefined interim analysis of 30-day data, which has been previously published. In the present analysis, we present the final, 90-day data from OVID and we additionally investigate the impact of thromboprophylaxis on the resolution of symptoms.
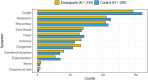
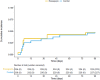
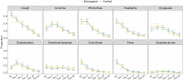
Results: Of the 472 patients included in the intention-to-treat population, 234 were randomised to receive enoxaparin and 238 no thromboprophylaxis. The median age was 57 (Q1-Q3: 53-62) years and 217 (46 %) were women. The 90-day primary outcome occurred in 11 (4.7 %) patients of the enoxaparin arm and in 11 (4.6 %) controls (adjusted relative risk 1.00; 95 % CI: 0.44-2.25): 3 events per group occurred after day 30. The 90-day incidence of cardiovascular events was 0.9 % in the enoxaparin arm vs. 1.7 % in controls (relative risk 0.51; 95 % CI: 0.09-2.75). Individual symptoms improved progressively within 90 days with no difference between groups. At 90 days, 42 (17.9 %) patients in the enoxaparin arm and 40 (16.8 %) controls had persistent respiratory symptoms.
Conclusions: In adult community patients with COVID-19, early thromboprophylaxis with enoxaparin did not improve the course of COVID-19 neither in terms of hospitalisation and death nor considering COVID-19-related symptoms.
Keywords: Anticoagulation; COVID-19; Heparin; SARS-CoV2; Thrombosis; Venous thromboembolism.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: Bernhard Gerber reports non-financial support and funding for an accredited continuing medical education programme from Axonlab, and Thermo Fisher Scientific; personal fees and funding for an accredited continuing medical education programme from Alnylam, Pfizer, and Sanofi; funding for an accredited continuing medical education programme from Bayer, Bristol Myers Squibb, Daiichi-Sankyo, Takeda, Octapharma, SOBI, Janssen, Novo Nordisk, Mitsubishi Pfizer, Tanabe Pharma, outside the submitted work. Stavros V. Konstantinides reports grants or contracts from Bayer AG; consulting fees from Bayer, Daiichi Sankyo, and Boston Scientific; and payment or honoraria from Bayer, INARI Medical, MSD, Pfizer, and Bristol-Myers Squibb. Stefan Stortecky reports research grants from Edwards Lifesciences to the institution, research grants from Medtronic to the institution, research grants from Boston Scientific to the institution, research grants from Abbott to the institution, personal fees from Boston Scientific, from Teleflex, from BTG –Boston Scientific outside the submitted work. Helia Robert-Ebadi reports speaker honoraria from Daichi-Sankyo, and Bayer. David Spirk reports employment by Sanofi-Aventis Switzerland. Daniel Duerschmied reports research support from German Research Foundation, CytoSorbents, Haemonetic; consulting and speaker's fees from Bayer Healthcare, Daiichi Sankyo, LEO Pharma, AstraZeneca, Boston Scientific, and BMS–Pfizer. Nils Kucher reports institutional research grants from Concept Medical, Bard, Bentley, Boston Scientific, INARI, Sanofi, and Bayer; and personal fees from Concept Medical, Bayer, Boston Scientific, and INARI. Stefano Barco reports institutional research grants from Concept Medical, Bard, Bentley, Boston Scientific, INARI, Sanofi, and Bayer; and personal fees from Concept Medical, Bayer, Boston Scientific, and INARI. All other authors do not report any conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Bikdeli B., Madhavan M.V., Jimenez D., Chuich T., Dreyfus I., Driggin E., Nigoghossian C., Ageno W., Madjid M., Guo Y., Tang L.V., Hu Y., Giri J., Cushman M., Quéré I., Dimakakos E.P., Gibson C.M., Lippi G., Favaloro E.J., Fareed J., Caprini J.A., Tafur A.J., Burton J.R., Francese D.P., Wang E.Y., Falanga A., McLintock C., Hunt B.J., Spyropoulos A.C., Barnes G.D., Eikelboom J.W., Weinberg I., Schulman S., Carrier M., Piazza G., Beckman J.A., Steg P.G., Stone G.W., Rosenkranz S., Goldhaber S.Z., Parikh S.A., Monreal M., Krumholz H.M., Konstantinides S.V., Weitz J.I., Lip G.Y.H. COVID-19 and thrombotic or thromboembolic disease: implications for prevention, antithrombotic therapy, and follow-up: JACC state-of-the-art review. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020;75:2950–2973. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2020.04.031. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Klok F.A., Kruip M., van der Meer N.J.M., Arbous M.S., Gommers D., Kant K.M., Kaptein F.H.J., van Paassen J., Stals M.A.M., Huisman M.V., Endeman H. Confirmation of the high cumulative incidence of thrombotic complications in critically ill ICU patients with COVID-19: an updated analysis. Thromb. Res. 2020;191:148–150. doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2020.04.041. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gupta A., Madhavan M.V., Sehgal K., Nair N., Mahajan S., Sehrawat T.S., Bikdeli B., Ahluwalia N., Ausiello J.C., Wan E.Y., Freedberg D.E., Kirtane A.J., Parikh S.A., Maurer M.S., Nordvig A.S., Accili D., Bathon J.M., Mohan S., Bauer K.A., Leon M.B., Krumholz H.M., Uriel N., Mehra M.R., Elkind M.S.V., Stone G.W., Schwartz A., Ho D.D., Bilezikian J.P., Landry D.W. Extrapulmonary manifestations of COVID-19. Nat. Med. 2020;26:1017–1032. doi: 10.1038/s41591-020-0968-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

