Overall survival and toxicity of Y90 radioembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma patients in Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer stage C (BCLC-C)
- PMID: 36396989
- PMCID: PMC9670475
- DOI: 10.1186/s12876-022-02528-y
Overall survival and toxicity of Y90 radioembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma patients in Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer stage C (BCLC-C)
Abstract
Introduction: National Comprehensive Cancer Network HCC guidelines recommend Y90 to treat BCLC-C patients only in select cases given the development of systemic regimens. We sought to identify ideal candidates for Y90 by assessing survival and toxicities in this patient group.
Materials and methods: The Radiation-Emitting Selective Internal radiation spheres in Non-resectable tumor registry is a prospective observational study (NCT: 02,685,631). Patients with advanced HCC were stratified into 3 groups based on tumor location, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status, and liver function. Group 1: liver isolated HCC, ECOG 0 and Child Pugh (CP) A (n = 12, 16%), Group 2: liver isolated HCC, ECOG ≥ 1 or CP B/C (n = 37, 49%), and Group 3: extrahepatic HCC with any ECOG or CP score (n = 26, 35%). Patients in any group could have macrovascular invasion. Overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS) with 95% confidence intervals (95% CI) were calculated. Grade 3 + toxicities were tracked using Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events v5. Cox proportional hazard model was performed to determine factors affecting OS.
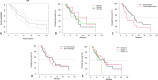
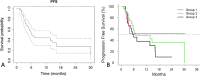
Results: Seventy-five BCLC-C patients treated between 2015 and 2019 were reviewed. The groups were similar in age, sex, race, and ethnicity (all p > 0.05). Bilobar disease was least common in Group 1 (p < 0.001). Median OS of the entire cohort was 13.6 (95% CI 7.5-16.1) months. Median OS of Groups 1-3 were 21.8, 13.1 and 11.5 months respectively (p = 0.6). Median PFS for the cohort was 6.3 (4.8-14.7) months. Median PFS for group 1 was not reached. Mean PFS for Group 1 was 17.3 ± 4.8 months. Median PFS for Groups 2 and 3 was 6.8 and 5.9 months (X2 = 1.5, p = 0.5). Twenty-four Grade 3 or greater toxicities developed, most commonly hyperbilirubinemia (8/75, 11%) and thrombocytopenia (2/75, 3%). The incidence of toxicities between groups was similar (all p > 0.05). Cox Proportional Hazard analysis predicted shorter OS with CP class B/C (X2 = 6.7, p = 0.01), while macrovascular invasion (X2 = 0.5, p = 0.5) and ECOG score of ≥ 1 (X2 = 2.1, p = 0.3) was not associated with OS.
Conclusions: OS of CPA patients with advanced HCC and performance status of 0 was 21.8 months following Y90. CP A cirrhosis is the best predictor of prolonged OS in advanced (BCLC-C) HCC.
Keywords: Adult; Carcinoma, hepatocellular carcinoma; Treatment outcome; Yttrium radioisotopes/ adverse events; Yttrium radioisotopes/ therapeutic use.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Ripal T. Gandhi is a consultant and speaker for Sirtex Medical and serves as a proctor for Sirtex Medical. Zachary S. Collins has received an institutional research grant from Sirtex Medical and serves as a speaker and consultant for Sirtex Medical. Jayson S. Brower is a consultant for Sirtex Medical. Daniel Y. Sze has received institutional research grants from Sirtex Medical and Boston Scientific. He was a consultant and has received support for travel/hotel/meals for meetings with Sirtex Medical and Boston Scientific. Andrew S. Kennedy has received institutional support from Sirtex Medical. Jafar Golzarian is a consultant for Sirtex Medical and Boston Scientific. He has also received institutional grant support from Sirtex Medical. Eric A. Wang is a proctor for Sirtex Medical. Daniel B. Brown has received institutional research support from Sirtex Medical and Guerbet. He has served as a speaker for Cook Medical and a Data Safety Monitor for Bard Medical. The other authors do not have a conflict to report.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Multicenter Evaluation of Survival and Toxicities of Hepatocellular Carcinoma following Radioembolization: Analysis of the RESiN Registry.J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2021 Jun;32(6):845-852. doi: 10.1016/j.jvir.2021.03.535. Epub 2021 Apr 2. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2021. PMID: 33812981
-
Overall survival and toxicity of hepatocellular carcinoma Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer B patients receiving Y90 radioembolization: analysis of the radiation-emitting SIR-spheres in non-resectable liver tumor (RESiN) registry.J Gastrointest Oncol. 2023 Apr 29;14(2):874-885. doi: 10.21037/jgo-22-972. Epub 2023 Mar 6. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37201079 Free PMC article.
-
Yttrium-90 Radioembolization for BCLC Stage C Hepatocellular Carcinoma Comparing Child-Pugh A Versus B7 Patients: Are the Outcomes Equivalent?Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2020 May;43(5):721-731. doi: 10.1007/s00270-020-02434-4. Epub 2020 Mar 5. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2020. PMID: 32140840
-
Development and validation of prognostic risk prediction models for hepatocellular carcinoma patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors based on a systematic review and meta-analysis of 47 cohorts.Front Immunol. 2023 Jul 14;14:1215745. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1215745. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37520554 Free PMC article.
-
Review of Use of Y90 as a Bridge to Liver Resection and Transplantation in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.J Gastrointest Surg. 2021 Oct;25(10):2690-2699. doi: 10.1007/s11605-021-05095-x. Epub 2021 Aug 3. J Gastrointest Surg. 2021. PMID: 34345997 Review.
Cited by
-
Selective internal radiation therapy across Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer (BCLC) stages of hepatocellular carcinoma: literature review.Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. 2024 Dec 1;13(6):974-990. doi: 10.21037/hbsn-23-504. Epub 2024 Jun 6. Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39669087 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Impact of Radiation Dose and Tumour Burden on Outcomes in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: 11-Year Experience in a 413-Patient Cohort Treated with Yttrium-90 Resin Microsphere Radioembolisation.Liver Cancer. 2024 Sep 19;14(2):158-179. doi: 10.1159/000541539. eCollection 2025 Apr. Liver Cancer. 2024. PMID: 40255874 Free PMC article.
-
Eco-Friendly Approaches in Oncology: Developing Holmium (166Ho) Glass Microspheres for Hepatocellular Radioembolization.ACS Omega. 2025 May 14;10(22):22426-22433. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c08734. eCollection 2025 Jun 10. ACS Omega. 2025. PMID: 40521516 Free PMC article.
-
Transarterial Radioembolisation with Y90 Resin Microspheres and the Effect of Reimbursement Criteria in France: Final Results of the CIRT-FR Prospective Observational Study.Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2025 Feb;48(2):205-220. doi: 10.1007/s00270-024-03955-y. Epub 2025 Jan 14. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2025. PMID: 39809885 Free PMC article.
-
Intraperitoneal PD-1 monoclonal antibody for the treatment of advanced primary liver cancer with malignant ascites: a single-arm, single-center, phase Ib trial.ESMO Open. 2024 Jan;9(1):102206. doi: 10.1016/j.esmoop.2023.102206. Epub 2024 Jan 9. ESMO Open. 2024. PMID: 38194882 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Ferlay J, Colombet M, Soerjomataram I, Mathers C, Parkin DM , Pineros M, Znaor A, Bray F. Estimating the global cancer incidence and mortality in 2018: GLOBOCAN sources and methods. Int J Cancer, 2019; pp. 1941–1953. - PubMed
-
- Globocan 2020. Section of cancer surveillance, international agency for research on cancer, World Health Organization; 2020. [Online]. Available: https://gco.iarc.fr/today/data/factsheets/cancers/11-Liver-fact-sheet.pdf. [Accessed 17 March 2022].
-
- Llovet JM, Real MI, Montana X, Planas R, Coll S, Aponte J, Ayuso C, Sala M, Muchard J, Richard S, Rodes J, Barcelona Liver Cancer Group Arterial embolisation or chemoembolisation versus symptomatic treatment in patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2002;359(9319):1734–1739. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(02)08649-X. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

