Predictive value of the TyG index and rheumatoid factor for cardiovascular disease risk in a rheumatoid arthritis population: data from a survey of 418 patients
- PMID: 36397103
- PMCID: PMC9673431
- DOI: 10.1186/s12944-022-01735-6
Predictive value of the TyG index and rheumatoid factor for cardiovascular disease risk in a rheumatoid arthritis population: data from a survey of 418 patients
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the correlation between the triglyceride-glucose (TyG) index and rheumatoid factor levels and the existence of cardiovascular disease in patients in the rheumatoid arthritis population and to analyze their potential value in predicting the risk of cardiovascular disease.
Methods: Patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated by the Traditional Chinese Medicine Department of Rheumatism of the China-Japan Friendship Hospital from 2019-01 to 2021-12 were included in this retrospective study. Regression analysis was performed with multifactor-corrected multimodal logistic models to observe the correlation between the TyG index and rheumatoid factor and cardiovascular disease risk, construct predictive models and assess the potential predictive value of the variables on cardiovascular disease risk with receiver operating characteristic curves. The results were further corrected by sensitivity analysis and trend tests.
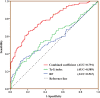
Results: A total of 418 patients with rheumatoid arthritis were included in the study. In the rheumatoid arthritis population, high rheumatoid factor (OR = 1.002, 95% CI = 1.001-1.002, P < 0.001), high TyG index (OR = 1.057, 95% CI = 1.008-1.109, P = 0.022), advanced age (OR = 1.080, 95% CI = 1.050-1.112, P < 0.001), and low physical activity (OR = 2.848, 95% CI = 1.195-6.785, P = 0.018) were independent risk factors for the existence of cardiovascular disease in patients. The combined coefficient calculated on the basis of the TyG index and rheumatoid factor was used to plot the receiver operating characteristic curve with an area under the curve of 0.791, which can be used to predict the potential risk of cardiovascular disease in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Further sensitivity analysis found that the marker of focus remained associated with cardiovascular disease risk in a high-physical activity population with rheumatoid arthritis. The final trend test found a linear trend between the TyG index, rheumatoid factor levels and the risk of cardiovascular disease.
Conclusion: In the rheumatoid arthritis population, the TyG index and rheumatoid factor have some potential predictive value in determining the risk of cardiovascular disease, and the predictive efficacy is better when the two tests are combined.
Keywords: Cardiovascular disease; Clinical prediction model; Rheumatoid arthritis; Rheumatoid factor; TyG index.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical