Endoscopic tympanoplasty type I using interlay technique
- PMID: 36397175
- PMCID: PMC9670569
- DOI: 10.1186/s40463-022-00597-3
Endoscopic tympanoplasty type I using interlay technique
Abstract
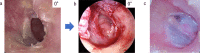
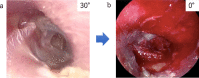
Background: Tympanoplasty using the interlay technique has rarely been reported in transcanal endoscopic ear surgery, unlike the underlay technique. This is because many surgeons find it challenging to detach the epithelial layer of the tympanic membrane using only one hand. However, the epithelial layer can be easily detached from the inferior part of the tympanic membrane. Another key point is to actively improve anteroinferior visibility even if the overhang is slight because most perforations and postoperative reperforations are found in the anteroinferior quadrant of the tympanic membrane. We report the application of the interlay technique in endoscopic tympanoplasty type I for tympanic perforations.
Methods: We retrospectively reviewed the medical records of 51 patients who had undergone tympanoplasty using the interlay technique without ossiculoplasty between 2017 and 2020. We then compared the data with those of patients who underwent microscopic surgery (MS) using the underlay technique between 1998 and 2009 (n = 104). No other technique was used in each group during this period. Repair of tympanic membrane perforation and hearing outcomes were assessed for > 1 year postoperatively.
Results: The perforation sites were limited to the anterior, posterior, and anterior-posterior quadrants in 23, 1, and 27 ears, respectively. Perforations were closed in 50 of the 51 ears (98.0%), and the postoperative hearing was good (average air-bone [A-B] gap was 6.8 ± 5.8 dB). The surgical success rate for the repair of tympanic membrane perforation was not significantly different from the MS group (93.3%, P = 0.15). The average postoperative average A-B gap in the group that underwent the interlay technique was significantly different from that in the MS group (10.1 ± 6.6 dB, P < 0.01).
Conclusion: The interlay technique should be considered as one of the treatment methods in endoscopic surgery for tympanic perforations. Further study of the postoperative outcomes of this procedure should be conducted to establish the optimal surgical procedure for tympanic perforations.
Trial registration: This study was retrospectively approved by the Institutional Review Board of the Jikei University, Tokyo, Japan (approval number: 32-205 10286). Video abstract.
Keywords: Chronic otitis media; Interlay technique; Middle ear surgery; Myringoplasty; Transcanal endoscopic ear surgery; Tympanic perforations.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Comparison of the clinical outcomes between endoscopic butterfly inlay cartilage tympanoplasty and underlay cartilage tympanoplasty in small-to-medium-sized tympanic membrane perforations].Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2025 Jun;39(6):528-533;541. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2025.06.006. Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2025. PMID: 40443375 Chinese.
-
Endoscopic Transcanal Myringoplasty for Anterior Perforations of the Tympanic Membrane.JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2016 Nov 1;142(11):1088-1093. doi: 10.1001/jamaoto.2016.2114. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2016. PMID: 27540858
-
Hearing results following endoscopic type I tympanoplasty in medium and large perforations.Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2025 Jan-Feb;91(1):101509. doi: 10.1016/j.bjorl.2024.101509. Epub 2024 Sep 10. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2025. PMID: 39388826 Free PMC article.
-
Totally endoscopic tympanic membrane repair.HNO. 2021 Oct;69(10):791-796. doi: 10.1007/s00106-021-01052-x. Epub 2021 May 26. HNO. 2021. PMID: 34041565 Review. English.
-
Endoscopic Techniques in Tympanoplasty.Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 2016 Oct;49(5):1253-64. doi: 10.1016/j.otc.2016.05.016. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 2016. PMID: 27565390 Review.
Cited by
-
Myringoplasty: A comparison of inlay and underlay techniques.J Otol. 2024 Apr;19(2):72-76. doi: 10.1016/j.joto.2024.04.004. Epub 2024 Oct 19. J Otol. 2024. PMID: 39720113 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical outcomes of type I endoscopic tympanoplasty: Over-Underlay vs. Overlay techniques in a randomized controlled trial.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2025 Jul 23. doi: 10.1007/s00405-025-09573-9. Online ahead of print. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2025. PMID: 40699222
-
Endoscopic Type 1 Tympanoplasty: Evaluation of Clinical Success and Hearing Improvement.Medeni Med J. 2024 Dec 27;39(4):268-274. doi: 10.4274/MMJ.galenos.2024.88278. Medeni Med J. 2024. PMID: 39726409 Free PMC article.
-
Bilateral Endoscopic Type 1 Tympanoplasty in a Single Session: Functional and Clinical Outcomes.Turk Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2025 Mar 28;62(4):138-144. doi: 10.4274/tao.2024.2024-10-7. Turk Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2025. PMID: 40152405 Free PMC article.
-
Inside-out raising mucosal-tympanomeatal flap approach for the repair of large marginal perforations.BMC Surg. 2023 Dec 13;23(1):378. doi: 10.1186/s12893-023-02286-y. BMC Surg. 2023. PMID: 38093229 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

