Coexistence of condyloma acuminatum and extramammary Paget's disease on penis and scrotum: A rare case report
- PMID: 36397375
- PMCID: PMC9666121
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000031754
Coexistence of condyloma acuminatum and extramammary Paget's disease on penis and scrotum: A rare case report
Abstract
Rationale: Extramammary Paget's disease (EMPD) is a rare skin cancer that commonly occurs in sites rich in apocrine glands, such as perineum, vulva, axilla, scrotum, and penis. On the other hand, condyloma acuminatum (CA; also referred to as anogenital warts) is a common benign neoplasm caused by human papillomavirus. Few cases of coexistent EMPD and CA have been reported because of the rarity of the condition.
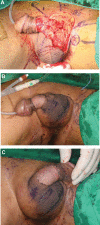
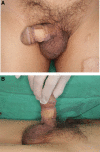
Patient concerns and diagnosis: A 72-year-old man with a genital mass, which appeared to be composed of multiple papillomatous masses, was referred for surgical resection. The lesion was first noticed 6 months previously and grew rapidly. CO2 ablative laser therapy was performed twice at a primary clinic, but the mass recurred.
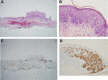
Intervention and outcomes: Excisional biopsy revealed the presence of coexistent EMPD and CA. Additional wide excision was performed, and postoperative biopsy confirmed no residual tumor. Two years after surgery, no recurrence had occurred.
Lessons: CA can co-occur with several types of skin malignancies, and a skin malignancy coexisting with CA is difficult to diagnose visually. Therefore, even if a skin lesion in the genital region is considered to be CA, we recommend punch biopsy before treatment because it can benefit prognosiss.
Copyright © 2022 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no funding and conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Pigmented extramammary Paget's disease accompanied with condyloma acuminatum: a case report].Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2018 Jun 18;50(3):572-575. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2018. PMID: 29930432 Chinese.
-
Simultaneous human papillomavirus 6 (HPV 6) -positive condyloma acuminatum, HPV 31-positive Bowen's disease, and non HPV-associated extramammary Paget's disease coexisting within an area presenting clinically as condyloma acuminatum.Am J Dermatopathol. 2005 Oct;27(5):439-42. doi: 10.1097/01.dad.0000157463.57087.6a. Am J Dermatopathol. 2005. PMID: 16148417
-
Extramammary Paget's Disease of the Scrotal and Penile: A Case Report and Review of the Literature.Urol Int. 2024;108(3):264-271. doi: 10.1159/000536654. Epub 2024 Feb 17. Urol Int. 2024. PMID: 38368870 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extramammary Paget's disease not only mimicking but also accompanying condyloma acuminatum. A case report.Dermatology. 2005;210(4):315-8. doi: 10.1159/000084756. Dermatology. 2005. PMID: 15942218
-
Extramammary Paget's Disease: Diagnosis, Pathogenesis, and Treatment with Focus on Recent Developments.Curr Oncol. 2021 Aug 5;28(4):2969-2986. doi: 10.3390/curroncol28040260. Curr Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34436026 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A rare case of extramammary Paget disease in a young HIV-positive man.JAAD Case Rep. 2023 Nov 18;43:24-26. doi: 10.1016/j.jdcr.2023.11.004. eCollection 2024 Jan. JAAD Case Rep. 2023. PMID: 38162408 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Zhang N, Gong K, Zhang X, et al. . Extramammary Paget’s disease of scrotum – report of 25 cases and literature review. Urol Oncol. 2010;28:28–33. - PubMed
-
- Perrotto J, Abbott JJ, Ceilley RI, et al. . The role of immunohistochemistry in discriminating primary from secondary extramammary Paget disease. Am J Dermatopathol. 2010;32:137–43. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

