Ferulic Acid Induces NURR1 Expression and Promotes Dopaminergic Differentiation in Neural Precursor Cells
- PMID: 36397809
- PMCID: PMC9653552
- DOI: 10.22088/IJMCM.BUMS.11.1.78
Ferulic Acid Induces NURR1 Expression and Promotes Dopaminergic Differentiation in Neural Precursor Cells
Abstract
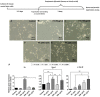
Degeneration of dopaminergic (DA) neurons in the substantia nigra is known as the main cause of Parkinson's disease (PD). Preventing the loss of DA neurons alongside the cell-replacement therapy have brought tremendous hope for the treatment of PD. For this purpose, various studies have been done to find the specific DA neuro-protective compounds or progressing DA-differentiation methods. Ferulic acid (FA) has strong neuro-protective effects, but at this point its role on protection and differentiation of DA neurons is not well-defined. Mouse neural stem cells (mNSCs) were treated with FA and expressions of TH (tyrosine hydroxylase) and NURR1 as the DA neuron specific markers were determined using real time qRT-PCR and immunostaining assays . Finally, efficacy of FA on DA differentiation was evaluated in comparison with other methods using fibroblast growth factor 8b (FGF8b) and sonic hedgehog (SHH). Treatment with FA could increase the Th and Nurr1 gene expressions in mNSCs. Also, it enhanced β - tubullin - III expression and increased the neurite length in treated groups. Real time qRT-PCR and immunostaining assays showed that FA could increase DA differentiation in mNSCs effectively. Also, gene expression profile in some groups showed that FA can raise the differentiation rate of other neuronal subtypes such as cholinergic neurons. FA effectively induces the DA differentiation in neural precursor cells by its ability to increase the expression of the NURR1 transcription factor, which is a known transcription factor for differentiation of midbrain DA neurons.
Keywords: Dopaminergic; Ferulic acid; Nurr1; Tyrosine hydroxylase; differentiation; neural stem cell.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Kaur R, Mehan S, Singh S. Understanding multifactorial architecture of Parkinson's disease: pathophysiology to management. Neurol Sci. 2019;40:13–23. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
