A Comparative Study of Intravenous Dexmedetomidine with Local Infiltration of Ropivacaine in Attenuation of Stress Response to Skull Pin Insertion in Craniotomies
- PMID: 36398172
- PMCID: PMC9665997
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0042-1757221
A Comparative Study of Intravenous Dexmedetomidine with Local Infiltration of Ropivacaine in Attenuation of Stress Response to Skull Pin Insertion in Craniotomies
Abstract
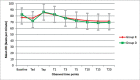
Objective Skull pin insertion in patients undergoing craniotomies elicits hemodynamic and neuroendocrine stress response that may be deleterious to the patient. Various drugs and techniques have been documented in literature to abate this stress response. Against this background, we aimed to compare the efficacy of intravenous dexmedetomidine and local infiltration of ropivacaine for attenuation of stress response to pin insertion in craniotomies. Methods Eighty-eight adult patients undergoing craniotomy under general anesthesia from March 2019 to April 2020 requiring application of head holder were randomized into two equal groups. After intubation, 0.75 µg kg -1 of dexmedetomidine over 10 minutes through infusion was given in group D, while local infiltration at pin sites was done with 0.5% ropivacaine, 2 mL at each site in group R. Hemodynamic parameters and levels of serum cortisol, prolactin, and blood glucose were measured before and after pin insertion. Unpaired t -test for continuous variables and Mann-Whitney U test was used for nonnormally distributed variables. Results Heart rate was statistically similar between the two groups at all the observed time points. The difference in mean arterial pressure values between the two groups was found to be statistically significant only from 10 to 20 minutes after pin insertion being statistically similar at rest of the time points. Levels of serum glucose, cortisol, and prolactin values 30 minutes after pin insertion were statistically similar between both groups. Conclusion We concluded that both interventions are equally efficacious in attenuation of hemodynamic and stress response to head holder application in patients undergoing craniotomies.
Keywords: craniotomy; dexmedetomidine; hemodynamics; ropivacaine.
Asian Congress of Neurological Surgeons. This is an open access article published by Thieme under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonDerivative-NonCommercial License, permitting copying and reproduction so long as the original work is given appropriate credit. Contents may not be used for commercial purposes, or adapted, remixed, transformed or built upon. ( https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/ ).
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Misra S, Koshy T, Unnikrishnan K P, Suneel P R, Chatterjee N. Gabapentin premedication decreases the hemodynamic response to skull pin insertion in patients undergoing craniotomy. J Neurosurg Anesthesiol. 2011;23(02):110–117. - PubMed
-
- Bithal P K, Dash H H, Chauhan R S, Mohanty B. Haemodynamic changes in response to skull-pins application- comparison between normotensive and hypertensive patients. Indian J Anaesth. 2002;46:381–383.
-
- Uyar A S, Yagmurdur H, Fidan Y, Topkaya C, Basar H. Dexmedetomidine attenuates the hemodynamic and neuroendocrinal responses to skull-pin head-holder application during craniotomy. J Neurosurg Anesthesiol. 2008;20(03):174–179. - PubMed
-
- Mushtaq K, Ali Z, Shal N F, Syed S, Naqash I, Ramzan A U. A randomised study to compare the effectiveness of intravenous dexmedetomedine with placebo to attenuate the haemodynamic and neuroendocrine responses to fixation of skull pin head holder for craniotomy. Nothern Journal of ISA. 2016;1:16–23.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous