Ghrelin alleviates depression-like behaviour in rats subjected to high-fat diet and diurnal rhythm disturbance
- PMID: 36398212
- PMCID: PMC9641471
Ghrelin alleviates depression-like behaviour in rats subjected to high-fat diet and diurnal rhythm disturbance
Abstract
Objectives: In the era of globalization, a sedentary lifestyle is highly linked with obesity and neurobehavioral complications such as depression. While depression is associated with dopamine dysfunction in the ventral tegmental area (VTA), ghrelin enhances the dopaminergic activity in the VTA. Therefore, the present study aimed to assess the effect of ghrelin on depression-like behaviour in rats subjected to a high-fat diet (HFD) and disturbed diurnal rhythm (DDR) for 45 days.
Methods: The neurobehavioral deficits resulting from HFD and DDR in rats, and the behaviour modulation by intra-VTA administration of ghrelin, alone or in combination with ghrelin receptor antagonist were confirmed by evaluation of behavioural parameters in the elevated plus-maze, forced swim test, open field test, and rotarod assessment. Further, the levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin-1β (IL-1β) and IL-6, oxidative stress marker malondialdehyde (MDA), and antioxidants enzymes like superoxide dismutase (SOD), reduced glutathione (GSH), and catalase (CAT) were measured.
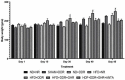
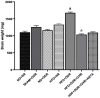
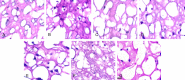
Results: The levels of TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, and MDA were increased in the brain of HFD and DDR exposed rats, while that of SOD, GSH, and CAT were reduced. Intra-VTA ghrelin administration from day 41-45 to the HFD and DDR exposed rats improved cognitive behaviour and physical activity confirming the antidepressant effect. Moreover, ghrelin restored the levels of SOD, GSH and CAT efficiently, and reduced that of MDA, TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6, which signifies its protective effect.
Conclusion: Overall, this study confirmed the ameliorative effect of ghrelin in HFD- and DDR-induced depression-like behaviour.
Keywords: High-fat diet; cytokines; depression; diurnal rhythm disturbance; ghrelin.
AJTR Copyright © 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Oxidative stress-induced cognitive impairment in obesity can be reversed by vitamin D administration in rats.Nutr Neurosci. 2018 Dec;21(10):744-752. doi: 10.1080/1028415X.2017.1348436. Epub 2017 Jul 6. Nutr Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 28683595
-
Unacylated ghrelin stimulates steroidogenesis in lean rats and reverses reproductive dysfunction in high fat diet-fed rats.Syst Biol Reprod Med. 2019 Apr;65(2):129-146. doi: 10.1080/19396368.2018.1523971. Epub 2018 Sep 28. Syst Biol Reprod Med. 2019. PMID: 30265152
-
Effect of Forced Physical Activity on the Severity of Experimental Colitis in Normal Weight and Obese Mice. Involvement of Oxidative Stress and Proinflammatory Biomarkers.Nutrients. 2019 May 21;11(5):1127. doi: 10.3390/nu11051127. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 31117199 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of leptin, ghrelin, and neuropeptide-Y on serum Tnf-Α, Il-1β, Il-6, Fgf-2, galanin levels and oxidative stress in an experimental generalized convulsive seizure model.Neuropeptides. 2017 Feb;61:31-37. doi: 10.1016/j.npep.2016.08.002. Epub 2016 Aug 6. Neuropeptides. 2017. PMID: 27522536
-
Cinnamaldehyde Mitigates Atherosclerosis Induced by High-Fat Diet via Modulation of Hyperlipidemia, Oxidative Stress, and Inflammation.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 Jun 21;2022:4464180. doi: 10.1155/2022/4464180. eCollection 2022. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022. PMID: 35774377 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Relationship Between Obesity and Depression Considering the Inflammatory Theory.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 22;26(11):4966. doi: 10.3390/ijms26114966. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40507778 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ghrelin/GHSR System in Depressive Disorder: Pathologic Roles and Therapeutic Implications.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 Jul 10;46(7):7324-7338. doi: 10.3390/cimb46070434. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 39057075 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Pathologic Roles and Therapeutic Implications of Ghrelin/GHSR System in Mental Disorders.Depress Anxiety. 2024 Nov 26;2024:5537319. doi: 10.1155/2024/5537319. eCollection 2024. Depress Anxiety. 2024. PMID: 40226675 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A link between ghrelin and major depressive disorder: a mini review.Front Psychiatry. 2024 Mar 13;15:1367523. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2024.1367523. eCollection 2024. Front Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 38544844 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lower ghrelin in depression might be connected to the absence of psychotic-like experiences.Endocr Connect. 2025 Aug 27;14(8):e250263. doi: 10.1530/EC-25-0263. Print 2025 Aug 1. Endocr Connect. 2025. PMID: 40823927 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hoare E, Jacka F, Berk M. The impact of urbanization on mood disorders: an update of recent evidence. Curr Opin Psychiatry. 2019;32:198–203. - PubMed
-
- Bekris S, Antoniou K, Daskas S, Papadopoulou-Daifoti Z. Behavioural and neurochemical effects induced by chronic mild stress applied to two different rat strains. Behav Brain Res. 2005;161:45–59. - PubMed
-
- Elizalde N, Gil-Bea FJ, Ramírez MJ, Aisa B, Lasheras B, Del Rio J, Tordera RM. Long-lasting behavioral effects and recognition memory deficit induced by chronic mild stress in mice: effect of antidepressant treatment. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2008;199:1–14. - PubMed
-
- Grippo AJ, Beltz TG, Johnson AK. Behavioral and cardiovascular changes in the chronic mild stress model of depression. Physiol Behav. 2003;78:703–710. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
