Vascular endothelial growth factor-C in activating vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-3 and chemokine receptor-4 in melanoma adhesion
- PMID: 36398426
- PMCID: PMC9716217
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.17571
Vascular endothelial growth factor-C in activating vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-3 and chemokine receptor-4 in melanoma adhesion
Abstract
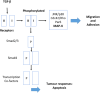
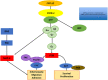
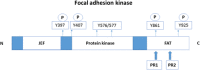
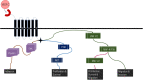
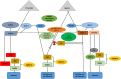
Vascular endothelial growth factor-C (VEGF-C) binds to receptor vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-3 (VEGFR-3) expressed on lymphatic endothelial and melanoma cells. Binding of VEGF-C to VEGFR-3 enhances receptor phosphorylation that activates mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAP-K) and phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K). These signalling pathways regulate cell migration and adhesion in response to internal or external changes. In addition, the overexpression of VEGF-C upregulates chemokine receptor CXCR-4 in tumours (melanoma). CXCR-4 is expressed on cells of the immune system (natural killer cells) and facilitates the migration of leukocytes in response to the CXCL12 ligand. The latter is expressed by lymphatic endothelial cells and by stromal cells in the tumour microenvironment (TME). The gradient established between CXCR-4 expressed on tumour cells and CXCL12 produced by stromal and lymphatic endothelial cells enhances tumour cell metastasis. 3-(4-Dimethylamino-naphthalen-1-ylmethylene)-1, 3-dihydroindol-2-one, MAZ-51, is an indolinone-based synthetic molecule that inhibits the phosphorylation of the tyrosine kinase receptor VEGFR-3. CTCE-9908, a CXCR-4 antagonist derived from human CXCL12, hinders receptor phosphorylation and the subsequent signalling pathways that would be activated. VEGF-C is stimulated by transforming growth factor-beta 1 (TGF-β1), which facilitates cell-cell and cell-matrix adhesion by regulating cadherins through the activation of focal adhesion kinase (FAK) and mediates paxillin upregulation. Increased VEGF-C protein levels stimulated by TGF-β bound to VEGFR-3 impact on intracellular pathways that promote tumour cell adhesion. In addition, increased VEGF-C protein levels lead to enhanced CXCR-4 protein expression. Therefore, effective blocking of VEGR-3 and CXCR-4 may inhibit tumour cell metastasis by hampering intracellular proteins promoting adhesion.
© 2022 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the compiling, authorship and/or publication of this manuscript.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Decoding the synergistic potential of MAZ-51 and zingerone as therapy for melanoma treatment in alignment with sustainable development goals.Cell Biochem Funct. 2024 Mar;42(2):e3950. doi: 10.1002/cbf.3950. Cell Biochem Funct. 2024. PMID: 38348768 Review.
-
Endothelin-1 induces the transactivation of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-3 and modulates cell migration and vasculogenic mimicry in melanoma cells.J Mol Med (Berl). 2013 Mar;91(3):395-405. doi: 10.1007/s00109-012-0956-2. Epub 2012 Sep 11. J Mol Med (Berl). 2013. Retraction in: J Mol Med (Berl). 2024 Nov;102(11):1411. doi: 10.1007/s00109-024-02484-y. PMID: 22965194 Retracted.
-
Sunitinib inhibits lymphatic endothelial cell functions and lymph node metastasis in a breast cancer model through inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3.Breast Cancer Res. 2011 Jun 21;13(3):R66. doi: 10.1186/bcr2903. Breast Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 21693010 Free PMC article.
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation and recruitment to new focal adhesions of focal adhesion kinase and paxillin in endothelial cells.J Biol Chem. 1997 Jun 13;272(24):15442-51. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.24.15442. J Biol Chem. 1997. PMID: 9182576
-
The role of the VEGF-C/VEGFR-3 axis in cancer progression.Br J Cancer. 2007 Feb 26;96(4):541-5. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6603487. Epub 2006 Dec 12. Br J Cancer. 2007. PMID: 17164762 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring Phytochemical Adjuvant Therapy in Melanoma Treatment: The Effects of MAZ-51 and Zingerone on Melanoma Cell Proliferation.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2025 Sep;52(9):e70059. doi: 10.1111/1440-1681.70059. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2025. PMID: 40695356 Free PMC article.
-
Integrin and Its Associated Proteins as a Mediator for Mechano-Signal Transduction.Biomolecules. 2025 Jan 23;15(2):166. doi: 10.3390/biom15020166. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40001469 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PIEZO1 Promotes the Migration of Endothelial Cells via Enhancing CXCR4 Expression under Simulated Microgravity.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 1;25(13):7254. doi: 10.3390/ijms25137254. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39000362 Free PMC article.
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor-C and its receptor-3 signaling in tumorigenesis.3 Biotech. 2023 Oct;13(10):326. doi: 10.1007/s13205-023-03719-4. Epub 2023 Sep 1. 3 Biotech. 2023. PMID: 37663750 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PPARs and the Kynurenine Pathway in Melanoma-Potential Biological Interactions.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 4;24(4):3114. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043114. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36834531 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- National Cancer Institute Surveillanc EaERP . Cancer stat facts: Melanoma of the skin. 2020; https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/melan.html
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

