Diabetic hyperglycemia promotes primary tumor progression through glycation-induced tumor extracellular matrix stiffening
- PMID: 36399580
- PMCID: PMC9674287
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abo1673
Diabetic hyperglycemia promotes primary tumor progression through glycation-induced tumor extracellular matrix stiffening
Abstract
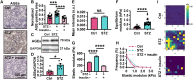
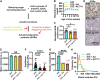
Diabetes mellitus is a complex metabolic disorder that is associated with an increased risk of breast cancer. Despite this correlation, the interplay between tumor progression and diabetes, particularly with regard to stiffening of the extracellular matrix, is still mechanistically unclear. Here, we established a murine model where hyperglycemia was induced before breast tumor development. Using the murine model, in vitro systems, and patient samples, we show that hyperglycemia increases tumor growth, extracellular matrix stiffness, glycation, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of tumor cells. Upon inhibition of glycation or mechanotransduction in diabetic mice, these same metrics are reduced to levels comparable with nondiabetic tumors. Together, our study describes a novel biomechanical mechanism by which diabetic hyperglycemia promotes breast tumor progression via glycating the extracellular matrix. In addition, our work provides evidence that glycation inhibition is a potential adjuvant therapy for diabetic cancer patients due to the key role of matrix stiffening in both diseases.
Figures






References
-
- Ozer K., Horsanali M. O., Gorgel S. N., Ozbek E., Diabetes is an important risk factor for metastasis in non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 17, 105–108 (2016). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- IK6 BX005240/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- F31 HL154727/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- I01 BX002025/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- P50 CA098131/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL127499/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA068485/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK114809/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U24 DK059637/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK119212/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK101003/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM131178/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- F99 CA274695/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

