Three-Year Update of Tisagenlecleucel in Pediatric and Young Adult Patients With Relapsed/Refractory Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in the ELIANA Trial
- PMID: 36399695
- PMCID: PMC10022844
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.22.00642
Three-Year Update of Tisagenlecleucel in Pediatric and Young Adult Patients With Relapsed/Refractory Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in the ELIANA Trial
Abstract
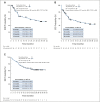
Clinical trials frequently include multiple end points that mature at different times. The initial report, typically based on the primary end point, may be published when key planned co-primary or secondary analyses are not yet available. Clinical Trial Updates provide an opportunity to disseminate additional results from studies, published in JCO or elsewhere, for which the primary end point has already been reported.In the primary analysis of the global phase II ELIANA trial (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT02435849), tisagenlecleucel provided an overall remission rate of 81% in pediatric and young adult patients with relapsed or refractory B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (R/R B-ALL), with 59% of responders remaining relapse-free at 12 months. Here, we report an update on efficacy, safety, and patient-reported quality of life in 79 pediatric and young adult patients with R/R B-ALL following a median follow-up of 38.8 months. The overall remission rate was 82%. The median event-free survival was 24 months, and the median overall survival was not reached. Event-free survival was 44% (95% CI, 31 to 57) and overall survival was 63% (95% CI, 51 to 73) at 3 years overall (most events occur within the first 2 years). The estimated 3-year relapse-free survival with and without censoring for subsequent therapy was 52% (95% CI, 37 to 66) and 48% (95% CI, 34 to 60), respectively. No new or unexpected long-term adverse events were reported. Grade 3/4 adverse events were reported in 29% of patients > 1 year after infusion; grade 3/4 infection rate did not increase > 1 year after infusion. Patients reported improvements in quality of life up to 36 months after infusion. These findings demonstrate favorable long-term safety and suggest tisagenlecleucel as a curative treatment option for heavily pretreated pediatric and young adult patients with R/R B-ALL.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Comment in
-
CAR T-Cells for Cure in Pediatric B-ALL.J Clin Oncol. 2023 Mar 20;41(9):1646-1648. doi: 10.1200/JCO.22.02345. Epub 2023 Jan 12. J Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36634289 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
More Updates to Come of Tisagenlecleucel in Pediatric and Young Adult Patients With Relapsed/Refractory Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in the ELIANA Trial: Could the Statistical Methodology Be Further Improved?J Clin Oncol. 2023 May 1;41(13):2450-2451. doi: 10.1200/JCO.22.02839. Epub 2023 Mar 10. J Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36898080 No abstract available.
-
Chimeric antigen receptor T-cells in B-acute lymphoblastic leukemia: history, current situation, and future.Transl Pediatr. 2023 Oct 30;12(10):1900-1907. doi: 10.21037/tp-23-366. Epub 2023 Oct 27. Transl Pediatr. 2023. PMID: 37969122 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Three-year update outcomes of the first chimeric antigen receptor-T therapy for children and young adults with relapsed/refractory acute lymphoblastic leukemia.Transl Pediatr. 2024 Apr 30;13(4):535-536. doi: 10.21037/tp-23-535. Epub 2024 Apr 8. Transl Pediatr. 2024. PMID: 38715679 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Crotta A, Zhang J, Keir C: Survival after stem-cell transplant in pediatric and young-adult patients with relapsed and refractory B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Curr Med Res Opin 34:435-440, 2018 - PubMed
-
- KYMRIAH [prescribing information]. East Hanover, NJ: Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation, 2022
-
- Grupp SA, Maude SL, Rives S, et al. : Updated analysis of the efficacy and safety of tisagenlecleucel in pediatric and young adult patients with relapsed/refractory (r/r) acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 132, 2018. (suppl 1; abstr 895)
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

