The role of the immune microenvironment in bone, cartilage, and soft tissue regeneration: from mechanism to therapeutic opportunity
- PMID: 36401295
- PMCID: PMC9675067
- DOI: 10.1186/s40779-022-00426-8
The role of the immune microenvironment in bone, cartilage, and soft tissue regeneration: from mechanism to therapeutic opportunity
Abstract
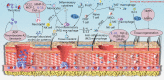
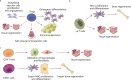
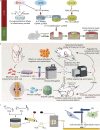
Bone, cartilage, and soft tissue regeneration is a complex spatiotemporal process recruiting a variety of cell types, whose activity and interplay must be precisely mediated for effective healing post-injury. Although extensive strides have been made in the understanding of the immune microenvironment processes governing bone, cartilage, and soft tissue regeneration, effective clinical translation of these mechanisms remains a challenge. Regulation of the immune microenvironment is increasingly becoming a favorable target for bone, cartilage, and soft tissue regeneration; therefore, an in-depth understanding of the communication between immune cells and functional tissue cells would be valuable. Herein, we review the regulatory role of the immune microenvironment in the promotion and maintenance of stem cell states in the context of bone, cartilage, and soft tissue repair and regeneration. We discuss the roles of various immune cell subsets in bone, cartilage, and soft tissue repair and regeneration processes and introduce novel strategies, for example, biomaterial-targeting of immune cell activity, aimed at regulating healing. Understanding the mechanisms of the crosstalk between the immune microenvironment and regeneration pathways may shed light on new therapeutic opportunities for enhancing bone, cartilage, and soft tissue regeneration through regulation of the immune microenvironment.
Keywords: Biomaterials; Cell-cell interaction; Immune microenvironment; Regeneration; Tissue engineering.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Shin CS, Cabrera FJ, Lee R, Kim J, Ammassam Veettil R, Zaheer M, et al. 3D-bioprinted inflammation modulating polymer scaffolds for soft tissue repair. Adv Mater. 2021;33(4):e2003778. - PubMed
-
- Zhao Y, Song S, Ren X, Zhang J, Lin Q, Zhao Y. Supramolecular adhesive hydrogels for tissue engineering applications. Chem Rev. 2022;122(6):5604–40. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

