Organelle-targeted therapies: a comprehensive review on system design for enabling precision oncology
- PMID: 36402753
- PMCID: PMC9675787
- DOI: 10.1038/s41392-022-01243-0
Organelle-targeted therapies: a comprehensive review on system design for enabling precision oncology
Abstract
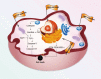
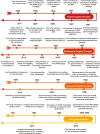
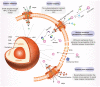
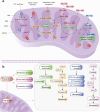
Cancer is a major threat to human health. Among various treatment methods, precision therapy has received significant attention since the inception, due to its ability to efficiently inhibit tumor growth, while curtailing common shortcomings from conventional cancer treatment, leading towards enhanced survival rates. Particularly, organelle-targeted strategies enable precise accumulation of therapeutic agents in organelles, locally triggering organelle-mediated cell death signals which can greatly reduce the therapeutic threshold dosage and minimize side-effects. In this review, we comprehensively discuss history and recent advances in targeted therapies on organelles, specifically including nucleus, mitochondria, lysosomes and endoplasmic reticulum, while focusing on organelle structures, organelle-mediated cell death signal pathways, and design guidelines of organelle-targeted nanomedicines based on intervention mechanisms. Furthermore, a perspective on future research and clinical opportunities and potential challenges in precision oncology is presented. Through demonstrating recent developments in organelle-targeted therapies, we believe this article can further stimulate broader interests in multidisciplinary research and technology development for enabling advanced organelle-targeted nanomedicines and their corresponding clinic translations.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

