BRAF activation by metabolic stress promotes glycolysis sensitizing NRASQ61-mutated melanomas to targeted therapy
- PMID: 36402789
- PMCID: PMC9675737
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-34907-0
BRAF activation by metabolic stress promotes glycolysis sensitizing NRASQ61-mutated melanomas to targeted therapy
Abstract
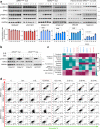
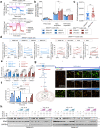
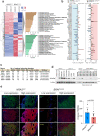
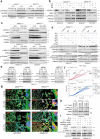
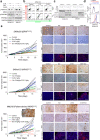
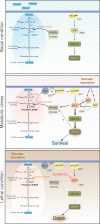
NRAS-mutated melanoma lacks a specific line of treatment. Metabolic reprogramming is considered a novel target to control cancer; however, NRAS-oncogene contribution to this cancer hallmark is mostly unknown. Here, we show that NRASQ61-mutated melanomas specific metabolic settings mediate cell sensitivity to sorafenib upon metabolic stress. Mechanistically, these cells are dependent on glucose metabolism, in which glucose deprivation promotes a switch from CRAF to BRAF signaling. This scenario contributes to cell survival and sustains glucose metabolism through BRAF-mediated phosphorylation of 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase-2/3 (PFKFB2/PFKFB3). In turn, this favors the allosteric activation of phosphofructokinase-1 (PFK1), generating a feedback loop that couples glycolytic flux and the RAS signaling pathway. An in vivo treatment of NRASQ61 mutant melanomas, including patient-derived xenografts, with 2-deoxy-D-glucose (2-DG) and sorafenib effectively inhibits tumor growth. Thus, we provide evidence for NRAS-oncogene contributions to metabolic rewiring and a proof-of-principle for the treatment of NRASQ61-mutated melanoma combining metabolic stress (glycolysis inhibitors) and previously approved drugs, such as sorafenib.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

