The diminution and modulation role of water-soluble gallic acid-carboxymethyl chitosan conjugates against the induced nephrotoxicity with cisplatin
- PMID: 36402822
- PMCID: PMC9675851
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-21681-8
The diminution and modulation role of water-soluble gallic acid-carboxymethyl chitosan conjugates against the induced nephrotoxicity with cisplatin
Abstract
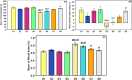
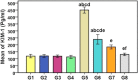
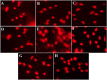
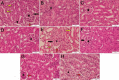
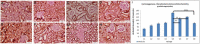
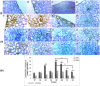
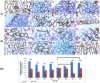
The toxicity of cisplatin (CDDP) toward the renal tubules and its severe effects on the proximal tubules limits its further use in cancer therapy. The current study was undertaken to evaluate the protective effects of gallic acid-grafted O-carboxymethyl chitosan (GA@CMCS) against nephrotoxicity induced by CDDP in rats. Renal injury was assessed in the GA@CMCS/CDDP-treated rats using kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1). Moreover, the levels of reduced glutathione (GSH), malondialdehyde (MDA), and nitric oxide (NO) were measured. The comet assay was performed to measure the DNA damage. The renoprotective activity of GA@CMCS was supported by histo- and immuno-pathological studies of the kidney. GA@CMCS significantly normalized the increases in kidney homogenate of KIM-1, MDA, and NO-induced by CDDP and significantly increased GSH as compared with the CDDP group. GA@CMCS also significantly protects rat kidneys from CDDP-induced histo- and immuno-pathological changes. Both biochemical findings and histo- and immuno-pathological evidence showed the renoprotective potential of GA@CMCS against CDDP-induced oxidative stress, inflammation, and renal dysfunction in rats. In conclusion, GA@CMCS has been shown to mitigate the nephrotoxicity impact of CDDP in cancer therapy.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

