Searching glycolate oxidase inhibitors based on QSAR, molecular docking, and molecular dynamic simulation approaches
- PMID: 36402831
- PMCID: PMC9675741
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-24196-4
Searching glycolate oxidase inhibitors based on QSAR, molecular docking, and molecular dynamic simulation approaches
Abstract
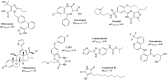
Primary hyperoxaluria type 1 (PHT1) treatment is mainly focused on inhibiting the enzyme glycolate oxidase, which plays a pivotal role in the production of glyoxylate, which undergoes oxidation to produce oxalate. When the renal secretion capacity exceeds, calcium oxalate forms stones that accumulate in the kidneys. In this respect, detailed QSAR analysis, molecular docking, and dynamics simulations of a series of inhibitors containing glycolic, glyoxylic, and salicylic acid groups have been performed employing different regression machine learning techniques. Three robust models with less than 9 descriptors-based on a tenfold cross (Q2 CV) and external (Q2 EXT) validation-were found i.e., MLR1 (Q2 CV = 0.893, Q2 EXT = 0.897), RF1 (Q2 CV = 0.889, Q2 EXT = 0.907), and IBK1 (Q2 CV = 0.891, Q2 EXT = 0.907). An ensemble model was built by averaging the predicted pIC50 of the three models, obtaining a Q2 EXT = 0.933. Physicochemical properties such as charge, electronegativity, hardness, softness, van der Waals volume, and polarizability were considered as attributes to build the models. To get more insight into the potential biological activity of the compouds studied herein, docking and dynamic analysis were carried out, finding the hydrophobic and polar residues show important interactions with the ligands. A screening of the DrugBank database V.5.1.7 was performed, leading to the proposal of seven commercial drugs within the applicability domain of the models, that can be suggested as possible PHT1 treatment.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures












References
-
- Wettschereck, D., Aha, D. W. & Mohri, T. A review and empirical evaluation of feature weighting methods for a class of lazy learning algorithms. Artif. Intell. Rev. 11, 273–314 (1997)
-
- Watts RWE, Danpure CJ, De Pauw L, Toussaint C, European Study Group on Transplantation in Hyperoxaluria Type 1 Combined liver-kidney and isolated liver transplantations for primary hyperoxaluria type 1: The european experience. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 1991;6:502–511. doi: 10.1093/ndt/6.7.502. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

