Conventional and drug-eluting beads transarterial chemoembolization in patients with unresectable intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: a systematic review and pooled analysis
- PMID: 36402872
- PMCID: PMC11797085
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-022-04485-1
Conventional and drug-eluting beads transarterial chemoembolization in patients with unresectable intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: a systematic review and pooled analysis
Abstract
Purpose: Patients with unresectable intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC) have poor survival. Conventional transarterial chemoembolization (c-TACE) and drug-eluting beads transarterial chemoembolization (DEB-TACE) are two treatment options for ICC, and this systematic review describes the efficacy of each of these modalities for unresectable ICC to guide clinical practice.
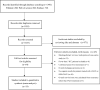
Methods: A literature search was performed in PubMed, Web of Science, and Embase databases regarding transhepatic arterial chemoembolization for intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. The Newcastle-Ottawa quality assessment Scale (NOS) was used to assess the risk of bias. Tumor response, disease control, and 1-, 2-, 3-year overall survival rate were pooled for estimation.
Results: The number of initial search results was 1035, and 19 articles met the inclusion criteria for this study after the screening. A total of 23 study cohorts and 1091 patients were provided. The pooled objective response rate (ORR) for c-TACE and DEB-TACE treating ICC was 29.4% (95% CI 11.6-50.8%) and 51.2% (95% CI 30.6-71.7%), respectively; disease control rate (DCR) was 72.8% (95% CI 55.6-87.3%) and 88.7% (95% CI 78.8-96.2%), respectively. The pooled survival rate at 1 year, 2 year, and 3 year was 49.7% (95% CI 39.1-60.3%), 24.0% (95% CI 12.6-37.3%), and 23.5% (95% CI 11.1-38.7%) for c-TACE; 58.6% (95% CI 44.2-72.3%), 26.7% (95% CI 18.1-36.3%), and 16.2% (95% CI 6.0-29.4%) for DEB-TACE.
Conclusion: The descriptive analysis suggested that DEB-TACE treatment for ICC may have better tumor response and disease control rates than c-TACE treatment, but the impact on overall survival was not demonstrated significantly by DEB-TACE treatment.
Keywords: Bile ducts cancer; Chemotherapy; Interventional oncology; Intra-arterial therapies; Meta-analysis.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose. Neither the entire paper nor any part of its content has been submitted to any other journal.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous