GediNET for discovering gene associations across diseases using knowledge based machine learning approach
- PMID: 36402891
- PMCID: PMC9675776
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-24421-0
GediNET for discovering gene associations across diseases using knowledge based machine learning approach
Abstract
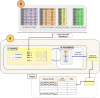
The most common approaches to discovering genes associated with specific diseases are based on machine learning and use a variety of feature selection techniques to identify significant genes that can serve as biomarkers for a given disease. More recently, the integration in this process of prior knowledge-based approaches has shown significant promise in the discovery of new biomarkers with potential translational applications. In this study, we developed a novel approach, GediNET, that integrates prior biological knowledge to gene Groups that are shown to be associated with a specific disease such as a cancer. The novelty of GediNET is that it then also allows the discovery of significant associations between that specific disease and other diseases. The initial step in this process involves the identification of gene Groups. The Groups are then subjected to a Scoring component to identify the top performing classification Groups. The top-ranked gene Groups are then used to train a Machine Learning Model. The process of Grouping, Scoring and Modelling (G-S-M) is used by GediNET to identify other diseases that are similarly associated with this signature. GediNET identifies these relationships through Disease-Disease Association (DDA) based machine learning. DDA explores novel associations between diseases and identifies relationships which could be used to further improve approaches to diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment. The GediNET KNIME workflow can be downloaded from: https://github.com/malikyousef/GediNET.git or https://kni.me/w/3kH1SQV_mMUsMTS .
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





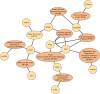
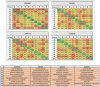
Similar articles
-
miRdisNET: Discovering microRNA biomarkers that are associated with diseases utilizing biological knowledge-based machine learning.Front Genet. 2023 Jan 12;13:1076554. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.1076554. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 36712859 Free PMC article.
-
microBiomeGSM: the identification of taxonomic biomarkers from metagenomic data using grouping, scoring and modeling (G-S-M) approach.Front Microbiol. 2023 Nov 22;14:1264941. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1264941. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 38075911 Free PMC article.
-
Robust biomarker screening from gene expression data by stable machine learning-recursive feature elimination methods.Comput Biol Chem. 2022 Oct;100:107747. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2022.107747. Epub 2022 Jul 29. Comput Biol Chem. 2022. PMID: 35932551
-
Knowledge-based approaches to drug discovery for rare diseases.Drug Discov Today. 2022 Feb;27(2):490-502. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2021.10.014. Epub 2021 Oct 27. Drug Discov Today. 2022. PMID: 34718207 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Application of Biological Domain Knowledge Based Feature Selection on Gene Expression Data.Entropy (Basel). 2020 Dec 22;23(1):2. doi: 10.3390/e23010002. Entropy (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33374969 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
TextNetTopics Pro, a topic model-based text classification for short text by integration of semantic and document-topic distribution information.Front Genet. 2023 Oct 5;14:1243874. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1243874. eCollection 2023. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 37867598 Free PMC article.
-
GeNetOntology: identifying affected gene ontology terms via grouping, scoring, and modeling of gene expression data utilizing biological knowledge-based machine learning.Front Genet. 2023 Aug 21;14:1139082. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1139082. eCollection 2023. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 37671046 Free PMC article.
-
PriPath: identifying dysregulated pathways from differential gene expression via grouping, scoring, and modeling with an embedded feature selection approach.BMC Bioinformatics. 2023 Feb 23;24(1):60. doi: 10.1186/s12859-023-05187-2. BMC Bioinformatics. 2023. PMID: 36823571 Free PMC article.
-
miRdisNET: Discovering microRNA biomarkers that are associated with diseases utilizing biological knowledge-based machine learning.Front Genet. 2023 Jan 12;13:1076554. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.1076554. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 36712859 Free PMC article.
-
Proteins Combined Score Prediction Based on Improved Gene Expression Programming Algorithm and Protein-Protein Interaction Network Characterization.IET Syst Biol. 2025 Jan-Dec;19(1):e70024. doi: 10.1049/syb2.70024. IET Syst Biol. 2025. PMID: 40522017 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Advances in translational bioinformatics: Computational approaches for the hunting of disease genes | Briefings in bioinformatics | Oxford academic. https://academic.oup.com/bib/article/11/1/96/193936 (Accessed 30 November 2021). - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

