Identification of potential targets of cinnamon for treatment against Alzheimer's disease-related GABAergic synaptic dysfunction using network pharmacology
- PMID: 36402912
- PMCID: PMC9675738
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-24378-0
Identification of potential targets of cinnamon for treatment against Alzheimer's disease-related GABAergic synaptic dysfunction using network pharmacology
Abstract
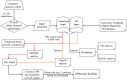
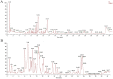
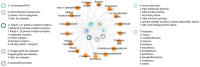
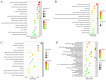
Cinnamon aqueous extract's active substance base remains unclear and its mechanisms, mainly the therapeutic target of anti-Alzheimer's disease (AD)-related GABAergic synaptic dysfunction, remain unclear. Here, 30 chemical components were identified in the aqueous extract of cinnamon using LC/MS; secondly, we explored the brain-targeting components of the aqueous extract of cinnamon, and 17 components had a good absorption due to the blood-brain barrier (BBB) limitation; thirdly, further clustering analysis of active ingredient targets by network pharmacology showed that the GABA pathway with GABRG2 as the core target was significantly enriched; then, we used prominent protein-protein interactions (PPI), relying on a protein-metabolite network, and identified the GABRA1, GABRB2 and GABRA5 as the closest targets to GABRG2; finally, the affinity between the target and its cognate active compound was predicted by molecular docking. In general, we screened five components, methyl cinnamate, propyl cinnamate, ( +)-procyanidin B2, procyanidin B1, and myristicin as the brain synapse-targeting active substances of cinnamon using a systematic strategy, and identified GABRA1, GABRB2, GABRA5 and GABRG2 as core therapeutic targets of cinnamon against Alzheimer's disease-related GABAergic synaptic dysfunction. Exploring the mechanism of cinnamon' activities through multi-components and multiple targets strategies promise to reduce the threat of single- target and symptom-based drug discovery failure.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Integration of Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking Technology Reveals the Mechanism of the Therapeutic Effect of Xixin Decoction on Alzheimer's Disease.Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2022;25(10):1785-1804. doi: 10.2174/1386207325666220523151119. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2022. PMID: 35616676
-
Mechanistic insight of the potential of geraniol against Alzheimer's disease.Eur J Med Res. 2022 Jun 14;27(1):93. doi: 10.1186/s40001-022-00699-8. Eur J Med Res. 2022. PMID: 35701806 Free PMC article.
-
Study on the Mechanism of Acori Graminei Rhizoma in the Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease Based on Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking.Biomed Res Int. 2021 Dec 24;2021:5418142. doi: 10.1155/2021/5418142. eCollection 2021. Biomed Res Int. 2021. PMID: 34977242 Free PMC article.
-
Cinnamon, a promising prospect towards Alzheimer's disease.Pharmacol Res. 2018 Apr;130:241-258. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2017.12.011. Epub 2017 Dec 16. Pharmacol Res. 2018. PMID: 29258915 Review.
-
Network pharmacology prediction and molecular docking-based strategy to explore the potential mechanism of Huanglian Jiedu Decoction against sepsis.Comput Biol Med. 2022 May;144:105389. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105389. Epub 2022 Mar 9. Comput Biol Med. 2022. PMID: 35303581 Review.
Cited by
-
Phytochemical Interactions with Calmodulin and Critical Calmodulin Binding Proteins Involved in Amyloidogenesis in Alzheimer's Disease.Biomolecules. 2023 Apr 15;13(4):678. doi: 10.3390/biom13040678. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 37189425 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Advances on the Analysis and Biological Functions of Cinnamaldehyde and Its Derivatives.Antioxidants (Basel). 2025 Jun 22;14(7):765. doi: 10.3390/antiox14070765. Antioxidants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40722869 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diet and lifestyle impact the development and progression of Alzheimer's dementia.Front Nutr. 2023 Jun 29;10:1213223. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1213223. eCollection 2023. Front Nutr. 2023. PMID: 37457976 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathway-based network medicine identifies novel natural products for Alzheimer's disease.Alzheimers Res Ther. 2025 Feb 14;17(1):43. doi: 10.1186/s13195-025-01694-x. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2025. PMID: 39953559 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 202210268242/Innovation Project for Undergraduates of Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine
- 82174003/the General Program of the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 21ZR1460900/Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai
- 02.ZY03.201913502N/Shanghai Municipal Key Special Project in the 13th Five-Year
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

