Clinical and radiological outcome of Mason-Johnston types III and IV radial head fractures treated by an on-table reconstruction
- PMID: 36403016
- PMCID: PMC9675101
- DOI: 10.1186/s13018-022-03394-w
Clinical and radiological outcome of Mason-Johnston types III and IV radial head fractures treated by an on-table reconstruction
Abstract
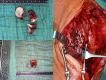
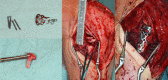
Background: Only few methods treating comminuted radial head fractures have been established providing sufficient joint reconstruction, restoring radial length and enabling early joint mobilization. When an anatomical reconstruction using open reduction and internal fixation is not possible, radial head resection or primary arthroplasty is often conducted. An "Ex situ/on-table" reconstruction is widely disregarded but can be an option. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the functional and radiological outcome of comminuted radial head fractures treated with an "on-table" reconstruction and internal fixation using a low profile plate.
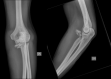
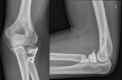
Methods: Fourteen patients who sustained a radial head fracture (9 Mason-Johnston type III and 5 Mason-Johnston type IV) and were treated with an "on-table" reconstruction between 2010 and 2020 were evaluated retrospectively. The patients mean age was 41.3 years (range 21-69). The clinical evaluation included active range of motion, grip strength, pain level and elbow stability. The functional outcome was assessed using the Disability of Arm, Shoulder and the Hand (DASH) score, Mayo Elbow Performance Index (MEPI), Broberg and Morrey score. The radiological examination included a.p. and lateral views of the injured elbow to evaluate nonunions, loss of reduction, joint alignment, avascular radial head necrosis, heterotopic ossifications and posttraumatic osteoarthritis.
Results: The inclusion rate was 74% with a mean follow-up of 50 months (range 16-128). The mean elbow flexion of the injured side was 126° (range110-145°) with an average extension loss of 8° (range 0-40°). Pronation was 65° (15-90°) and supination 66° (5-90°). The mean MEPI was 87 points (range 45-100). The mean DASH score was 13 points (range 1-88). According to the Broberg and Morrey functional scoring system, the average score was 92 points (range 88-100). Complete bone union was achieved in 9 cases, partial union in 4 cases and nonunion in one case. There were no signs of avascular necrosis of the radial head. Signs of post-traumatic osteoarthritis were seen in 11 cases. Five patients needed an implant removal due to a radio-ulnar impingement and one patient a revision surgery due to the nonunion and implant breakage.
Conclusions: An on-table (ex situ) reconstruction of the radial head is a reliable option with a good clinical outcome and low complication rate in the surgical treatment of comminuted radial head fractures. It can restore joint alignment and maintain radial length. The risk for avascular necrosis is neglectable, and the bone healing rate is high.
Keywords: Arthroplasty; Mason; On-table; Radial head fracture; Radial head resection; Reconstruction; Surgery; Treatment.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Clinical and functional outcomes of plate and screw osteosynthesis in mason type III and IV radial head fractures in the absence of a radial head prosthesis.Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2025 May 15;35(1):198. doi: 10.1007/s00590-025-04319-z. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2025. PMID: 40372555
-
Ex situ reconstruction of comminuted radial head fractures: is it truly worth a try?Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2019 Dec;139(12):1723-1729. doi: 10.1007/s00402-019-03250-3. Epub 2019 Aug 5. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2019. PMID: 31385021
-
Open reduction and internal fixation with bone grafts for comminuted mason type II radial head fractures.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2018 Aug 16;19(1):288. doi: 10.1186/s12891-018-2214-4. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2018. PMID: 30111311 Free PMC article.
-
Comminuted fractures of the radial head: comparison of resection and internal fixation. Surgical technique.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006 Mar;88 Suppl 1 Pt 1:11-23. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.E.00841. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006. PMID: 16510796 Review.
-
Radial Head Resection versus Arthroplasty in Unrepairable Comminuted Fractures Mason Type III and Type IV: A Systematic Review.Biomed Res Int. 2018 Jul 16;2018:4020625. doi: 10.1155/2018/4020625. eCollection 2018. Biomed Res Int. 2018. PMID: 30112387 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Analysis of Surgical Stabilization Results of Radial Head Fractures.J Clin Med. 2025 Feb 17;14(4):1336. doi: 10.3390/jcm14041336. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40004866 Free PMC article.
-
The clinical outcomes of open reduction and internal fixation for Mason-Johnston type IV fractures of the radial head.Front Surg. 2025 May 19;12:1506125. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2025.1506125. eCollection 2025. Front Surg. 2025. PMID: 40458192 Free PMC article.
-
A Study Evaluating the Functional Outcomes of Mason Type III and IV Radial Head Fractures Treated With a Radial Head Prosthesis.Cureus. 2024 Aug 14;16(8):e66898. doi: 10.7759/cureus.66898. eCollection 2024 Aug. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39280428 Free PMC article.
-
Which radial head fractures are best treated surgically?EFORT Open Rev. 2024 May 10;9(5):413-421. doi: 10.1530/EOR-24-0035. EFORT Open Rev. 2024. PMID: 38726982 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical and functional outcomes of plate and screw osteosynthesis in mason type III and IV radial head fractures in the absence of a radial head prosthesis.Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2025 May 15;35(1):198. doi: 10.1007/s00590-025-04319-z. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2025. PMID: 40372555
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

