Lactic acid modified rare earth-based nanomaterials for enhanced radiation therapy by disturbing the glycolysis
- PMID: 36403039
- PMCID: PMC9675198
- DOI: 10.1186/s12951-022-01694-1
Lactic acid modified rare earth-based nanomaterials for enhanced radiation therapy by disturbing the glycolysis
Abstract
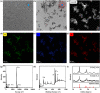
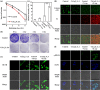
Deficient deposition of X-rays and strong capacity of repairing damage DNA of cancer cells limit the effect of radiation therapy (RT). Herein, we synthesize CsLu2F7 nanoparticles with lactic acid (LA) ligands (CsLu2F7-LA) to overcome these limitations. The high-Z atoms of Lu and Cs can deposit more X-rays for generating enhanced hydroxyl radicals (·OH). Meanwhile, the LA ligand will guide CsLu2F7-LA to target monocarboxylic acid transporter (MCT) and impede the transportation of free LA, leading to decreased glycolysis and DNA damage repair. Consequently, the curative effect of RT will be enhanced and the strategy of LA accumulation induced radiosensitization is proved by in vivo and in vitro experiments, which will bring prospects for enhanced RT with nanomedicine.
Keywords: Glycolysis; Lactic acid; Nanomedicine; Radiation therapy; Rare earth.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Interfering biosynthesis by nanoscale metal-organic frameworks for enhanced radiation therapy.Biomaterials. 2023 Apr;295:122035. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2023.122035. Epub 2023 Feb 2. Biomaterials. 2023. PMID: 36764193
-
Multifunctional high-Z nanoradiosensitizers for multimodal synergistic cancer therapy.J Mater Chem B. 2022 Mar 2;10(9):1328-1342. doi: 10.1039/d1tb02524d. J Mater Chem B. 2022. PMID: 35018941 Review.
-
Bi2WO6 Semiconductor Nanoplates for Tumor Radiosensitization through High- Z Effects and Radiocatalysis.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019 May 29;11(21):18942-18952. doi: 10.1021/acsami.9b03636. Epub 2019 May 15. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019. PMID: 31058495
-
[Effect of x-rays on the content of pyruvate and lactate of the blood and on the glycolysis of the bone marrow].Boll Soc Ital Biol Sper. 1952 Dec;28(12):1974-6. Boll Soc Ital Biol Sper. 1952. PMID: 13059150 Undetermined Language. No abstract available.
-
Emerging Nanotechnology and Advanced Materials for Cancer Radiation Therapy.Adv Mater. 2017 Aug;29(32). doi: 10.1002/adma.201700996. Epub 2017 Jun 23. Adv Mater. 2017. PMID: 28643452 Review.
Cited by
-
Theranostic applications of selenium nanomedicines against lung cancer.J Nanobiotechnology. 2023 Mar 20;21(1):96. doi: 10.1186/s12951-023-01825-2. J Nanobiotechnology. 2023. PMID: 36935493 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Nolan E, Bridgeman VL, Ombrato L, Karoutas A, Rabas N, Sewnath CAN, Vasquez M, Rodrigues FS, Horswell S, Faull P, et al. Radiation exposure elicits a neutrophil-driven response in healthy lung tissue that enhances metastatic colonization. Nat Cancer. 2022;3:173–187. doi: 10.1038/s43018-022-00336-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 82102190/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82072474/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 20191805/Shanghai Municipal Education Commission-Gaofeng Clinical Medicine Grant Support
- TMSK-2021-122/Foundation of National Facility for Translational Medicine (Shanghai)
- 2021YFC2501702/National Key R&D Program of China
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

