Inhibition of platelet-surface-bound proteins during coagulation under flow I: TFPI
- PMID: 36403087
- PMCID: PMC9822800
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2022.11.023
Inhibition of platelet-surface-bound proteins during coagulation under flow I: TFPI
Abstract
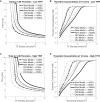
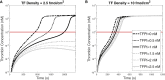
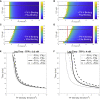
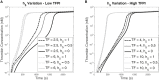
Blood coagulation is a self-repair process regulated by activated platelet surfaces, clotting factors, and inhibitors. Tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI) is one such inhibitor, well known for its inhibitory action on the active enzyme complex comprising tissue factor (TF) and activated clotting factor VII. This complex forms when TF embedded in the blood vessel wall is exposed by injury and initiates coagulation. A different role for TFPI, independent of TF:VIIa, has recently been discovered whereby TFPI binds a partially cleaved form of clotting factor V (FV-h) and impedes thrombin generation on activated platelet surfaces. We hypothesized that this TF-independent inhibitory mechanism on platelet surfaces would be a more effective platform for TFPI than the TF-dependent one. We examined the effects of this mechanism on thrombin generation by including the relevant biochemical reactions into our previously validated mathematical model. Additionally, we included the ability of TFPI to bind directly to and inhibit platelet-bound FXa. The new model was sensitive to TFPI levels and, under some conditions, TFPI could completely shut down thrombin generation. This sensitivity was due entirely to the surface-mediated inhibitory reactions. The addition of the new TFPI reactions increased the threshold level of TF needed to elicit a strong thrombin response under flow, but the concentration of thrombin achieved, if there was a response, was unchanged. Interestingly, we found that direct binding of TFPI to platelet-bound FXa had a greater anticoagulant effect than did TFPI binding to FV-h alone, but that the greatest effects occurred if both reactions were at play. The model includes activated platelets' release of FV species, and we explored the impact of varying the FV/FV-h composition of the releasate. We found that reducing the zymogen FV fraction of this pool, and thus increasing the fraction that is FV-h, led to acceleration of thrombin generation.
Copyright © 2022 Biophysical Society. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests K.L. received research support from Novo Nordisk.
Figures

References
-
- Camerer E., Kolstø A.B., Prydz H. Cell biology of tissue factor, the principal initiator of blood coagulation. Thromb. Res. 1996;81:1–41. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/004938489500209X - PubMed
-
- Furie B., Furie B.C. Molecular and cellular biology of blood coagulation. N. Engl. J. Med. 1992;326:800–806. - PubMed
-
- Maroney S.A., Ellery P.E., Mast A.E. Alternatively spliced isoforms of tissue factor pathway inhibitor. Thromb. Res. 2010;125:S52–S56. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0049384810000915 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Novotny W.F., Girard T.J., et al. Broze G.J. Platelets secrete a coagulation inhibitor functionally and antigenically similar to the lipoprotein associated coagulation inhibitor. Blood. 1988;72:2020–2025. https://ashpublications.org/blood/article/72/6/2020/166184/Platelets-sec... - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

