Exploring the mechanisms underlying the therapeutic effect of the Radix Bupleuri-Rhizoma Cyperi herb pair on hepatocellular carcinoma using multilevel data integration and molecular docking
- PMID: 36403263
- PMCID: PMC9740357
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.204388
Exploring the mechanisms underlying the therapeutic effect of the Radix Bupleuri-Rhizoma Cyperi herb pair on hepatocellular carcinoma using multilevel data integration and molecular docking
Abstract
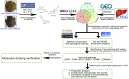
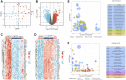
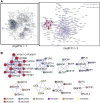
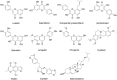
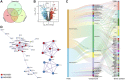
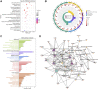
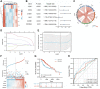
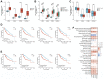
Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) is a promising and effective treatment for cancer with minimal side effects through a multi-active ingredient multitarget network. Radix Bupleuri and Rhizoma Cyperi are listed as herbs dispersing stagnated liver Qi in China. They have been used clinically to treat liver diseases for many years and recent pharmacological studies have shown that they inhibit the proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). However, the pharmacological mechanisms, potential targets, and clinical value of the Radix Bupleuri-Rhizoma Cyperi herb pair (CXP) for suppressing HCC growth have not been fully elucidated. We identified 44 CXP targets involved in the treatment of HCC using the GEO dataset and HERB database. An analysis of the Traditional Chinese Medicine System Pharmacology Database (TCMSP) showed that CXP exerts synergistic effects through 4 active ingredients, including quercetin, stigmasterol, isorhamnetin, and kaempferol. GO and KEGG analyses revealed that CXP mainly regulates HCC progression through metabolic pathways, the p53 signaling pathway, and the cell cycle. Additionally, we applied The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA)-liver hepatocellular carcinoma (LIHC) database to perform the expression patterns, clinical features, and prognosis of 6 genes (CCNB1, CDK1, CDK4, MYC, CDKN2A, and CHEK1) in cell cycle pathways to reveal that CXP suppresses HCC clinical therapeutic value. Moreover, based on molecular docking, we further verified that CXP exerts its anti-HCC activity through the interaction of multiple active components with cell cycle-related genes. We systematically revealed the potential pharmacological mechanisms and targets of CXP in HCC using multilevel data integration and molecular docking strategies.
Keywords: Radix Bupleuri-Rhizoma cyperi herb pair (CXP); cell cycle; hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC); molecular docking; traditional chinese medicine (TCM).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Fitzmaurice C, Abate D, Abbasi N, Abbastabar H, Abd-Allah F, Abdel-Rahman O, Abdelalim A, Abdoli A, Abdollahpour I, Abdulle ASM, Abebe ND, Abraha HN, Abu-Raddad LJ, et al., and Global Burden of Disease Cancer Collaboration. Global, Regional, and National Cancer Incidence, Mortality, Years of Life Lost, Years Lived With Disability, and Disability-Adjusted Life-Years for 29 Cancer Groups, 1990 to 2017: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. JAMA Oncol. 2019; 5:1749–68. 10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.2996 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

