Surface Engineering of Auxetic Scaffolds for Neural and Vascular Differentiation from Human Pluripotent Stem Cells
- PMID: 36403987
- PMCID: PMC9992167
- DOI: 10.1002/adhm.202202511
Surface Engineering of Auxetic Scaffolds for Neural and Vascular Differentiation from Human Pluripotent Stem Cells
Abstract
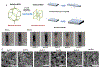
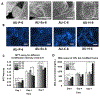
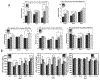
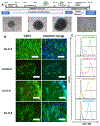
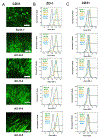
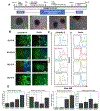
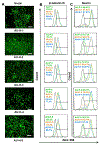
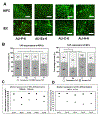
Auxetic materials are the materials that can display negative Poisson's ratio that describes the degree to which a material contracts (or expands) transversally when axially strained. Human stem cells sense the mechanical properties of the microenvironment, including material surface properties, stiffness, and Poisson's ratio. In this study, six different auxetic polyurethane (PU) foams with different elastic modulus (0.7-1.8 kPa) and Poisson's ratio (-0.1 to -0.5) are used to investigate lineage specification of human induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSCs). The surfaces of the foams are modified with chitosan or heparin to enhance the adhesion and proliferation of hiPSCs. Then, the vascular and neural differentiation of hiPSCs are investigated on different foams with distinct elastic modulus and Poisson's ratio. With different auxetic foams, cells show differential adherent density and differentiation capacity. Chitosan and heparin surface functionalization promote the hindbrain and hippocampal markers, but not forebrain markers during neural patterning of hiPSCs. Properly surface engineered auxetic scaffolds can also promote vascular differentiation of hiPSCs. This study represents a versatile and multifunctional scaffold fabrication approach and can lead to a suitable system for establishing hiPSC culture models in applications of neurovascular disease modeling and drug screening.
Keywords: Poisson's ratio; auxetic scaffolds; elastic modulus; human pluripotent stem cells; neural differentiation; vascular differentiation.
© 2022 Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest:
There is no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Lakes R, Science 1987, 235, 1038. - PubMed
-
- He C, Liu P, McMullan PJ, Griffin AC, physica status solidi (b) 2005, 242, 576
- Nkansah M, Evans K, Hutchinson I, Modelling and Simulation in Materials Science and Engineering 1994, 2, 337
- Gatt R, Zammit V, Caruana C, Grima JN, physica status solidi (b) 2008, 245, 502.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

