Concordance of Alzheimer's Disease-Related Biomarkers Between Intraventricular and Lumbar Cerebrospinal Fluid in Idiopathic Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus
- PMID: 36404546
- PMCID: PMC9881032
- DOI: 10.3233/JAD-220652
Concordance of Alzheimer's Disease-Related Biomarkers Between Intraventricular and Lumbar Cerebrospinal Fluid in Idiopathic Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus
Abstract
Background: Alzheimer's disease cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) biomarkers amyloid-β 1-42 (Aβ42), total tau (T-tau), and phosphorylated tau 181 (P-tau181) are widely used. However, concentration gradient of these biomarkers between intraventricular (V-CSF) and lumbar CSF (L-CSF) has been demonstrated in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus (iNPH), potentially affecting clinical utility.
Objective: Here we aim to provide conversion factors for clinical and research use between V-CSF and L-CSF.
Methods: Altogether 138 iNPH patients participated. L-CSF samples were obtained prior to shunt surgery. Intraoperative V-CSF samples were obtained from 97 patients. Post-operative follow-up L- and V-CSF (shunt reservoir) samples of 41 patients were obtained 1-73 months after surgery and then after 3, 6, and 18 months. CSF concentrations of Aβ42, T-tau, and P-tau181 were analyzed using commercial ELISA assays.
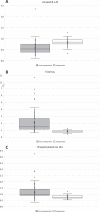
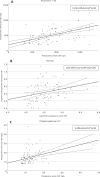
Results: Preoperative L-CSF Aβ42, T-tau, and P-tau181 correlated to intraoperative V-CSF (ρ= 0.34-0.55, p < 0.001). Strong correlations were seen between postoperative L- and V-CSF for all biomarkers in every follow-up sampling point (ρs Aβ42: 0.77-0.88, T-tau: 0.91-0.94, P-tau181: 0.94-0.96, p < 0.0001). Regression equations were determined for intraoperative V- and preoperative L-CSF (Aβ42: V-CSF = 185+0.34*L-CSF, T-tau: Ln(V-CSF) = 3.11+0.49*Ln(L-CSF), P-tau181: V-CSF = 8.2+0.51*L-CSF), and for postoperative V- and L-CSF (Aβ42: V-CSF = 86.7+0.75*L-CSF, T-tau: V-CSF = 86.9+0.62*L-CSF, P-tau181: V-CSF = 2.6+0.74*L-CSF).
Conclusion: Aβ42, T-tau, and P-tau181 correlate linearly in-between V- and L-CSF, even stronger after CSF shunt surgery. Equations presented here, provide a novel tool to use V-CSF for diagnostic and prognostic entities relying on the L-CSF concentrations and can be applicable to clinical use when L-CSF samples are not available or less invasively obtained shunt reservoir samples should be interpreted.
Keywords: Aβ42; P-tau; T-tau; biomarkers; idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors’ disclosures available online (
Figures


References
-
- Relkin N, Marmarou A, Klinge P, Bergsneider M, Black PM (2005) Diagnosing idiopathic normal-pressure hydrocephalus. Neurosurgery 57, S2–4–S2–16. - PubMed
-
- Mori E, Ishikawa M, Kato T, Kazui H, Miyake H, Miyajima M, Nakajima M, Hashimoto M, Kuriyama N, Tokuda T, Ishii K, Kaijima M, Hirata Y, Saito M, Arai H (2012) Guidelines for management of idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus: Second edition. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 52, 775–778. - PubMed
-
- Andrén K, Wikkelsø C, Tisell M, Hellström P (2014) Natural course of idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 85, 806–810. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

