Motion-robust, blood-suppressed, reduced-distortion diffusion MRI of the liver
- PMID: 36404637
- PMCID: PMC9792444
- DOI: 10.1002/mrm.29531
Motion-robust, blood-suppressed, reduced-distortion diffusion MRI of the liver
Abstract
Purpose: To evaluate feasibility and reproducibility of liver diffusion-weighted (DW) MRI using cardiac-motion-robust, blood-suppressed, reduced-distortion techniques.
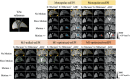
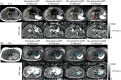
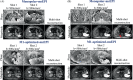
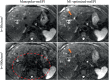
Methods: DW-MRI data were acquired at 3T in an anatomically accurate liver phantom including controlled pulsatile motion, in eight healthy volunteers and four patients with known or suspected liver metastases. Standard monopolar and motion-robust (M1-nulled, and M1-optimized) DW gradient waveforms were each acquired with single-shot echo-planar imaging (ssEPI) and multishot EPI (msEPI). In the motion phantom, apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) was measured in the motion-affected volume. In healthy volunteers, ADC was measured in the left and right liver lobes separately to evaluate ADC reproducibility between the two lobes. Image distortions were quantified using the normalized cross-correlation coefficient, with an undistorted T2-weighted reference.
Results: In the motion phantom, ADC mean and SD in motion-affected volumes substantially increased with increasing motion for monopolar waveforms. ADC remained stable in the presence of increasing motion when using motion-robust waveforms. M1-optimized waveforms suppressed slow flow signal present with M1-nulled waveforms. In healthy volunteers, monopolar waveforms generated significantly different ADC measurements between left and right liver lobes ( , reproducibility coefficients (RPC) = mm /s for monopolar-msEPI), while M1-optimized waveforms showed more reproducible ADC values ( , mm /s for M1-optimized-msEPI). In phantom and healthy volunteer studies, motion-robust acquisitions with msEPI showed significantly reduced image distortion ( ) compared to ssEPI. Patient scans showed reduction of wormhole artifacts when combining M1-optimized waveforms with msEPI.
Conclusion: Synergistic effects of combined M1-optimized diffusion waveforms and msEPI acquisitions enable reproducible liver DWI with motion robustness, blood signal suppression, and reduced distortion.
Keywords: diffusion; liver; motion-robust; multishot; phantom.
© 2022 The Authors. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
University of Wisconsin‐Madison receives departmental research support from GE Healthcare. Dr. Nataliya V. Uboha conducts consulting at QED, Taiho Inc., Incyte, AstraZeneca, Pfizer, Boston Gene, Helsinn, and Grail, obtains research funding from Taiho Inc, Ipsen, and EMD Serono, and has long position holdings at Natera and Exact Sciences. Dr. Ali Pirasteh provides consultancy at TheraCea, Sanofi Genzyme, and Otsuka. Dr. Arnaud Guidon is an employee of GE Healthcare. Dr. Diego Hernando is a Founder and part owner of Calimetrix, LLC.
Figures

References
-
- Chan JHM, Tsui EYK, Luk SH, et al. Diffusion‐weighted MR imaging of the liver: distinguishing hepatic abscess from cystic or necrotic tumor. Abdom Imag. 2001;26:161‐165. - PubMed
-
- Taouli B, Chouli M, Martin AJ, Qayyum A, Coakley FV, Vilgrain V. Chronic hepatitis: role of diffusion‐weighted imaging and diffusion tensor imaging for the diagnosis of liver fibrosis and inflammation. J Magnet Reson Imaging Offic J Int Soc Magn Reson Med. 2008;28:89‐95. - PubMed
-
- Taouli B, Koh DM. Diffusion‐weighted MR imaging of the liver. Radiology. 2010;254:47‐66. - PubMed
-
- Koh DM, Collins DJ. Diffusion‐weighted MRI in the body: applications and challenges in oncology. Am J Roentgenol. 2007;188:1622‐1635. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

