Recombinant Human Collagen-Based Bioinks for the 3D Bioprinting of Full-thickness Human Skin Equivalent
- PMID: 36404779
- PMCID: PMC9668586
- DOI: 10.18063/ijb.v8i4.611
Recombinant Human Collagen-Based Bioinks for the 3D Bioprinting of Full-thickness Human Skin Equivalent
Abstract
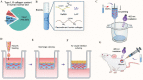
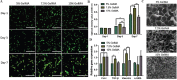
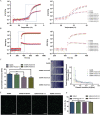
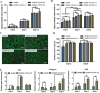
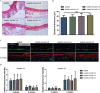
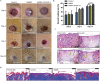
As a major extracellular matrix component within the skin, collagen has been widely used to engineer human skin tissues. However, most collagen is extracted from animals. Here, we introduced recombinant human type III collagen (rhCol3) as a bioactive component to formulate bioinks for the bioprinting of a full-thickness human skin equivalent. Human dermal fibroblasts were encapsulated in the gelatin methacryloyl-rhCol3 composite bioinks and printed on a transwell to form the dermis layer, on which human epidermal keratinocytes were seeded to perform an air-liquid interface culture for 6 weeks. After optimizing the bioink formulation and bioprinting process, we investigated the effect of rhCol3 on skin tissue formation. The results suggest that a higher concentration of rhCol3 would enhance the growth of both cells, resulting in a more confluent (~100%) spreading of the epidermal keratinocytes at an early stage (3 days), compared to the rhCol3-free counterpart. Moreover, in an in vivo experiment, adding rhCol3 in the hydrogel formulation would contribute to the skin wound healing process. Taken together, we conclude that rhCol3 could act as a functional bioink component to promote basic skin cellular processes for skin tissue engineering.
Keywords: 3D printing; Bioinks; Recombinant human collagen; Skin constructs.
Copyright: © 2022 Yang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Kanitakis J. Anatomy, histology and immunohistochemistry of normal human skin. Eur J Dermatol. 2002;12:390–9. - PubMed
-
- Gonzales KA, Fuchs E. Skin and its regenerative powers:An alliance between stem cells and their niche. Dev Cell. 2011;43:387–401. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2017.10.001. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fuchs E, Raghavan S. Getting under the skin of epidermal morphogenesis. Nat Rev Genet. 2002;3:199–209. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg758. - PubMed
-
- Watt FM, Huck W. Role of the extracellular matrix in regulating stem cell fate. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2013;14:467–73. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm3620. - PubMed
-
- Chung JH, Seo JY, Choi HR, et al. Modulation of skin collagen metabolism in aged and photoaged human skin in vivo. J Invest Dermatol. 2001;117:1218–24. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.0022-202x.2001.01544.x. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
