A Meta-analysis of ADIPOQ rs2241766 polymorphism association with type 2 diabetes
- PMID: 36404807
- PMCID: PMC9672214
- DOI: 10.1007/s40200-022-01086-0
A Meta-analysis of ADIPOQ rs2241766 polymorphism association with type 2 diabetes
Abstract
Objective: There is extensive research on the association between polymorphisms in the adiponectin gene (ADIPOQ) and type 2 diabetes (T2D). The present meta-analytic study explored the association between ADIPOQ rs2241766 polymorphisms and T2D.
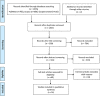
Metolds: Articles were collected by searching Google Scholar, Scopus, and PubMed electronic databases until 2021. They were searched using a systematic search of original and sensitive English keywords and their equivalent keywords based on the keywords "type 2 diabetes", "ADIPOQ", and "rs2241766". The article selection criteria were based on the PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses) flow diagram.
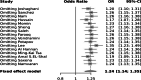
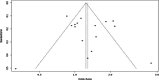
Results: The results revealed that there was no bias in this study. Some studies, such as Joshaghani et al. (odds ratio [OR] = 2.18), Hussain et al. (OR = 2.12), Momin (OR = 4.45), and Amal et al. (OR = 1.84), showed an increasing effect of ADIPOQ rs266729 polymorphism on T2D with 95% CI (P ˂ 0.01), while some have shown no significant association between them.
Conclusion: The results of this meta-analytic study showed the relationship between ADIPOQ and rs2241766. Also, it was found that Rs2241766 polymorphism and allele increase the risk, and rs2241766 increases the risk of developing T2D (OR = 1.29).
Keywords: ADIPOQ; Adiponectin gene; Diabetes mellitus; Type 2 diabetes; rs2241766.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Tehran University of Medical Sciences 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors state that there is no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this article.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Association of the ADIPOQ Rs2241766 and Rs266729 Polymorphisms with Metabolic Syndrome in the Chinese Population: A Meta-analysis.Biomed Environ Sci. 2016 Jul;29(7):505-15. doi: 10.3967/bes2016.066. Biomed Environ Sci. 2016. PMID: 27554120
-
Adiponectin (ADIPOQ) rs2241766 G/T polymorphism is associated with risk of cancer: evidence from a meta-analysis.Tumour Biol. 2013 Feb;34(1):493-504. doi: 10.1007/s13277-012-0574-1. Epub 2012 Nov 11. Tumour Biol. 2013. PMID: 23143890
-
Association between polymorphisms in the adiponectin gene and cardiovascular disease: a meta-analysis.BMC Med Genet. 2012 May 28;13:40. doi: 10.1186/1471-2350-13-40. BMC Med Genet. 2012. PMID: 22639977 Free PMC article.
-
A Systematic Narrative Review on ADIPOQ Gene Variants and its Association with T2DM in the Indian Population.Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2024;24(10):1161-1168. doi: 10.2174/0118715303257835231117062928. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2024. PMID: 38333969
-
Associations between two common single nucleotide polymorphisms (rs2241766 and rs1501299) of ADIPOQ gene and coronary artery disease in type 2 diabetic patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Oncotarget. 2017 May 31;8(31):51994-52005. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.18317. eCollection 2017 Aug 1. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28881706 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cell Therapy and Investigation of the Angiogenesis of Fibroblasts with Collagen Hydrogel on the Healing of Diabetic Wounds.Turk J Pharm Sci. 2023 Nov 7;20(5):302-309. doi: 10.4274/tjps.galenos.2022.62679. Turk J Pharm Sci. 2023. PMID: 37933815 Free PMC article.
-
Association of ADIPOQ Gene Polymorphisms with Type 2 Diabetes and Obesity Risk in the Kazakh Population: A Case-Control and Population-Based Study.Genes (Basel). 2024 May 23;15(6):669. doi: 10.3390/genes15060669. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38927605 Free PMC article.
-
Potential Association of The Pathogenic Kruppel-like Factor 14 (KLF14) and Adiponectin (ADIPOQ) SNVs with Susceptibility to T2DM.Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2024;24(9):1090-1100. doi: 10.2174/0118715303258744231117064253. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2024. PMID: 38031795
References
-
- Wdowiak A, Farahmandlou N, Tajik A, et al. The cytotoxic effect of estradiol Valerate, progesterone, and testosterone on brain glioblastoma (A172), colorectal Cancer (HT29) and human embryonic kidney (HEK293) cells and the expression levels of Bax, Bcl-2, and KAI-1/CD82 in A172 and HT29 cells. J B S. 2021;4(3):106–119.
-
- Norouzi S, Ahmadi R, Pashapour S. The cytotoxic effects of Tolmetin on evaluation of Bax and Bcl2 genes expression level in cervical cancer cells (Hela) KAUMS J (FEYZ) 2020;24(1):31–37.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

