Circulating salivary and serum miRNA-182, 320a, 375 and 503 expression levels in type 2 diabetes
- PMID: 36404826
- PMCID: PMC9672281
- DOI: 10.1007/s40200-022-01082-4
Circulating salivary and serum miRNA-182, 320a, 375 and 503 expression levels in type 2 diabetes
Abstract
Aim: Early-stage diagnosis of diabetes through non-invasive and diagnostic biofluid-like saliva has become a very popular approach to facilitate future preventive interventions and improve patient care. Meanwhile, the alteration of small non-coding RNA in human fluids has been suggested as a probable precedent for the early stages of diabetes.
Methods: In the present study, we checked the expression of miR-320a, 182-5p, 503, and 375 by using quantitative PCR in both stimulated and unstimulated saliva and blood samples of 40 adult patients with type-2 diabetes compared to 40 healthy individuals. In addition, we have sought to understand the possibility that miRNAs could provide new information about the status of type 2 diabetes in salivary samples beyond what can now be identified from blood samples and link their expression to the presence of clinically relevant risk factors. For this purpose, we have used a set of multivariate models.
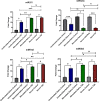
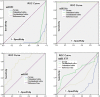
Results: The results showed that three miRNAs were more highly expressed in patients with type 2 diabetes, while miR-320-a was down-regulated in those patients compared to healthy subjects. Furthermore, the data showed that miR-320a was the most reliable predictor for distinguishing diabetic patients from healthy subjects, with AUCs of 0.997, 0.97, and 0.99 (97.4% sensitivity and 100% specificity, p = 0.001) for serum, unstimulated, and stimulated saliva samples, respectively.
Conclusions: Interestingly, the results of this study indicated that the amount of four miRNAs expressed in stimulated saliva was the same as in serum samples, which could conclude that specific miR-320a and 503 in stimulated saliva may introduce credible, non-invasive, and diagnostic biomarkers that can be used to monitor diabetic patients' status, while there is a need to design more research studies to confirm these findings.
Keywords: Salivary; Serum; Type 2 diabetes; microRNA.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Tehran University of Medical Sciences 2022, Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interestAuthors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identification of Serum Circulating MicroRNAs as Novel Diagnostic Biomarkers of Gastric Cancer.Front Genet. 2021 Feb 1;11:591515. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.591515. eCollection 2020. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 33597967 Free PMC article.
-
Elevated Plasma Levels of Circulating Extracellular miR-320a-3p in Patients with Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 May 15;21(10):3485. doi: 10.3390/ijms21103485. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32429037 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs miR-142-5p, miR-150-5p, miR-320a-3p, and miR-4433b-5p in Serum and Tissue: Potential Biomarkers in Sporadic Breast Cancer.Front Genet. 2022 Jun 30;13:865472. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.865472. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35846122 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of differentially expressed circulating serum microRNA for the diagnosis and prognosis of Indian non-small cell lung cancer patients.Curr Probl Cancer. 2020 Aug;44(4):100540. doi: 10.1016/j.currproblcancer.2020.100540. Epub 2020 Jan 23. Curr Probl Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32007320 Review.
-
Circulating microRNAs as predictive biomarkers of coronary artery diseases in type 2 diabetes patients.J Clin Lab Anal. 2022 May;36(5):e24380. doi: 10.1002/jcla.24380. Epub 2022 Mar 29. J Clin Lab Anal. 2022. PMID: 35349731 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Decreased Serum Levels of the Insulin Resistance-Related microRNA miR-320a in Patients with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 Apr 15;46(4):3379-3393. doi: 10.3390/cimb46040212. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38666942 Free PMC article.
-
Dysregulated microRNAs in type 2 diabetes and breast cancer: Potential associated molecular mechanisms.World J Diabetes. 2024 Jun 15;15(6):1187-1198. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v15.i6.1187. World J Diabetes. 2024. PMID: 38983808 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Assessment of salivary microRNA by RT-qPCR: Facing challenges in data interpretation for clinical diagnosis.PLoS One. 2024 Dec 10;19(12):e0314733. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0314733. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39656703 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Karolina DS, et al. miRNAs and diabetes mellitus. Expert Rev Endocrinol Metab. 2012;7(3):281–300. - PubMed
-
- Hsu Y-L, et al. Bone-marrow-derived cell-released extracellular vesicle miR-92a regulates hepatic pre-metastatic niche in lung cancer. Oncogene. 2020;39(4):739–753. - PubMed
-
- Kumar A, et al. Approach to sample size calculation in medical research. Curr Med Res Pract. 2014;4(2):87–92.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources