Effect of Costus pictus per se and in combination with Metformin and Enalapril in streptozotocin induced diabetic nephropathy in rats
- PMID: 36404856
- PMCID: PMC9672202
- DOI: 10.1007/s40200-022-01065-5
Effect of Costus pictus per se and in combination with Metformin and Enalapril in streptozotocin induced diabetic nephropathy in rats
Abstract
Aim: The present study was designed to investigate the effect of methanolic extract of Costus pictus (MECP) per se and in combination with drugs (Metformin and Enalapril) used in clinical practice in streptozotocin (STZ) induced diabetic nephropathy (DN) in rats.
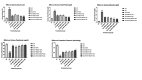
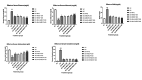
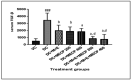
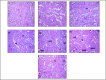
Methods: Diabetes was induced in male Wistar rats by a single injection of STZ (50 mg/kg i.p.). After 28 days diabetic rats were divided into six groups. Two groups were treated with MECP (200 mg/kg p.o.), MECP (400 mg/kg p.o.) respectively; one group was treated with metformin (225 mg/kg), enalapril (3.2 mg/kg) combination; and two groups were treated with a combination of metformin, enalapril and MECP (200 mg/kg) and combination of metformin, enalapril and MECP (400 mg/kg) respectively. One group was kept as diabetic control. At the end of the study, body weight, kidney weight, and kidney hypertrophy index were evaluated. Biochemical and antioxidant parameters were evaluated. TGF-β levels in serum were estimated. Histopathology of the kidney was also studied.
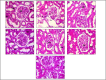
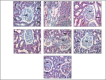
Results: The combination therapy showed a significant increase in the body weight, lowered blood glucose levels and ameliorated kidney hypertrophy index in STZ induced diabetic nephropathy in rats. It also normalized the altered levels of serum and urine parameters. Histopathological evaluation revealed that combination therapy reduced the vacuolar degeneration of tubules.
Conclusions: The results indicate that combination therapy of metformin, enalapril, and MECP has beneficial effects in management of diabetic nephropathy.
Keywords: Costus pictus; Diabetic Nephropathy; Enalapril; Metformin; Streptozotocin.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Tehran University of Medical Sciences 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestAuthors have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Laddha AP, Kulkarni YA. Tannins and vascular complications of Diabetes: An update [Internet]. Phytomedicine. Urban & Fischer; 2019 [cited 2019 Jan 14]. p. 229–45. Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0944711318305464. - PubMed
-
- Garud MS, Kulkarni YA. Gallic acid attenuates type I diabetic nephropathy in rats. Chem Biol Interact [Internet]. 2018 [cited 2018 Jun 26];282:69–76. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29331653. - PubMed
-
- Article R, Ayurvedic I, Journal M. Role of Traditional Medicine in Improving the Socio-Economic. 1986 [cited 2019 Jan 14]; Available from: www.aims.in.
-
- Majumdar M, Parihar PS. Antibacterial, antioxidant and antiglycation potential of Costus pictus from Southern region, India. Asian J Plant Sci Res [Internet] 2012;2:95–101.
-
- Don D, Remya R, Daniel M. Phytochemical and pharmacognostic investigation of antidiabetic Costus. 2012 [cited 2019 Jan 14];3:30–9. Available from: https://www.nresearchgate.net/publication/265877259.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

