The effect of exercise therapy on balance in patients with diabetic peripheral neuropathy: a systematic review
- PMID: 36404857
- PMCID: PMC9672244
- DOI: 10.1007/s40200-022-01077-1
The effect of exercise therapy on balance in patients with diabetic peripheral neuropathy: a systematic review
Abstract
Background: Peripheral sensory and motor nerves are often affected in people with diabetes mellitus (DM), and balance problems are widespread. Diabetic peripheral neuropathy is common. This study investigated the impact of exercise treatment on balance parameters in diabetic peripheral neuropathy patients.
Method: Electronic databases, such as PubMed, Web of Science, and Science Direct, were used to perform a search of accessible papers. The search strategy was (exercise therapy OR physical activity) AND (balance OR equilibrium OR postural control OR fall OR fall risk OR static balance OR dynamic balance OR functional balance) AND diabetic peripheral neuropathy. The Physiotherapy Evidence Database (PEDro) scale was used to rate the research in this review for its quality and reliability. Scores ranged from 5 to 9 on the PEDro scale.
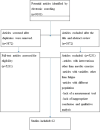
Result: According to databases, about 9,103 articles were found in August 2021 from March 1984 to February 2020. From 9103 articles, 3872 were deleted for different reasons, including duplicate, non-randomized controlled trial (RCT) articles and after reviewing the title and abstract. About 5,231 articles were found in free full text. In the end, 12 submissions were approved. These studies investigated the effects of exercise treatment on static, dynamic, and functional balance parameters in diabetic peripheral neuropathy patients.
Conclusions: This study showed the positive effects of balance and strengthening exercise on static balance indices in patients with diabetic peripheral neuropathy.
Supplementary information: The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1007/s40200-022-01077-1.
Keywords: Balance; Exercise therapy; Physical activity; Postural control; Type 2 diabetic neuropathy.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Tehran University of Medical Sciences 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe corresponding author states no conflict of interest on behalf of all authors.
References
-
- Rahbar S, Naimi SS, Reza Soltani A, Rahimi A, Akbarzadeh Baghban A, Rashedi V, et al. Improvement in biochemical parameters in patients with type 2 diabetes after twenty-four sessions of aerobic exercise: A randomized controlled trial. Iran Red Crescent Med J. 2017;19(7):2.
-
- Wild S, Roglic G, Green A, Sicree R, King H. Global prevalence of diabetes: estimates for the year 2000 and projections for 2030. Diabetes Care. 2004;27(5):1047–53. - PubMed
-
- Dyck PJ, Kratz K, Karnes J, Litchy WJ, Klein R, Pach J, et al. The prevalence by staged severity of various types of diabetic neuropathy, retinopathy, and nephropathy in a population-based cohort: the Rochester Diabetic Neuropathy Study. Neurology. 1993;43(4):817. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical