Cardioprotective effect of Hrudroga Chintamani Rasa in isoproterenol induced cardiotoxicity in male Sprague Dawley rats
- PMID: 36404861
- PMCID: PMC9672163
- DOI: 10.1007/s40200-022-01012-4
Cardioprotective effect of Hrudroga Chintamani Rasa in isoproterenol induced cardiotoxicity in male Sprague Dawley rats
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Cardioprotective effect of Hrudroga Chintamani Rasa in isoproterenol induced cardiotoxicity in male Sprague Dawley rats.J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2022 Jun 3;21(2):1271. doi: 10.1007/s40200-022-01060-w. eCollection 2022 Dec. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2022. PMID: 36409170 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Purpose: Ayurvedic system, a traditional medicinal system has mentioned a preparation Bruhat Vata Chintamani Rasa (Suvarnayukta) for management of heart diseases. Hrudroga Chintamani Rasa (HCR) is a formulation containing Bruhat Vata Chintamani Rasa and a few additional ingredients having beneficial effects in heart diseases. The present study was designed to investigate the cardioprotective activity of the Hrudroga Chintamani Rasa in isoproterenol (ISO)-induced myocardial infarction in rats.
Methods: Male Sprague Dawley rats were treated with HCR at a dose of 56.16 and 112.32 mg/kg for 30 days. Animals received ISO (85 mg/kg. s.c.) on 28th and 29th day at an interval of 24 h.
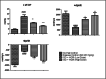
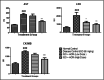
Result: Disease control animals treated with HCR at a dose of 56.16 mg/kg and 112.32 mg/kg to rats showed a significant reduction in elevated levels of aspartate aminotransferase (AST), lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), and creatine phosphokinase MB (CK-MB), and prevented loss of depleted antioxidant enzymes from the cardiac tissue. ISO-altered electrocardiogram pattern and haemodynamic parameters were also brought about to normal by treatment with HCR. HCR treatment also improved the levels of 5' adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) and Silent information regulator 1 (SIRT1) which have potent role in antioxidant defence mechanism. Histopathological findings also showed HCR treatment prevented cardiac tissue from damage.
Conclusion: HCR treatment showed a significant cardioprotective effect in ISO-induced cardiotoxicity in rats probably because of the potent antioxidant activity.
Supplementary information: The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1007/s40200-022-01012-4.
Keywords: Ayurvedic system; Cardio toxicity; Cardiovascular; Hrudroga Chintamani Rasa; Isoproterenol; Myocardial infarction.
© Springer Nature Switzerland AG 2022, corrected publication 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe author(s) declared the following potential conflict of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article: One of the co-author is from Shree Dhootapapeshwar Limited, which has funded the study. The first and corresponding author declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Correction to: Cardioprotective effect of Hrudroga Chintamani Rasa in isoproterenol induced cardiotoxicity in male Sprague Dawley rats.J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2022 Jun 3;21(2):1271. doi: 10.1007/s40200-022-01060-w. eCollection 2022 Dec. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2022. PMID: 36409170 Free PMC article.
-
Cardioprotective role of FA against isoproterenol induced cardiac toxicity.Mol Biol Rep. 2018 Oct;45(5):1357-1365. doi: 10.1007/s11033-018-4297-2. Epub 2018 Aug 13. Mol Biol Rep. 2018. PMID: 30105550
-
Preventive effect of nerolidol on isoproterenol induced myocardial damage in Wistar rats: Evidences from biochemical and histopathological studies.Drug Dev Res. 2019 Sep;80(6):814-823. doi: 10.1002/ddr.21564. Epub 2019 Jul 16. Drug Dev Res. 2019. PMID: 31313346
-
Dietary Phenolic Acids of Macrotyloma uniflorum (Horse Gram) Protect the Rat Heart Against Isoproterenol-Induced Myocardial Infarction.Phytother Res. 2016 Jul;30(7):1146-55. doi: 10.1002/ptr.5620. Epub 2016 Apr 19. Phytother Res. 2016. PMID: 27091200
-
Cardioprotective effect of HPLC standardized ethanolic extract of Terminalia pallida fruits against isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction in albino rats.J Ethnopharmacol. 2012 May 7;141(1):33-40. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2012.01.011. Epub 2012 Feb 1. J Ethnopharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22366678
References
-
- Prabhakaran D, Jeemon P, Roy A. Cardiovascular Diseases in India: Current Epidemiology and Future Directions. Circulation. Lippincott Williams and Wilkins. 2016;133:1605–20. Available from: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.114.008729 - PubMed
-
- Fan Y. Cardioprotective Effect of Rhapontigenin in Isoproterenol-Induced Myocardial Infarction in a Rat Model. Pharmacology. S. Karger AG. 2019;103:291–302. Available from: https://www.karger.com/Article/FullText/496800 - PubMed
-
- Burton KP, McCord JM, Ghai G. Myocardial alterations due to free-radical generation. Am J Physiol - Hear Circ Physiol. 1984;15. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/6331179/ - PubMed
-
- Rona G. Catecholamine cardiotoxicity. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1985;291–306. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/3894676/ - PubMed
-
- Amalraj A, Gopi S. Medicinal properties of Terminalia arjuna (Roxb.) Wight & Arn.: A review. J Tradit Complement Med National Tai wan University. 2017;65–78. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28053890/ - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

