Vedolizumab-Associated Hypereosinophilia and Hepatoxicity
- PMID: 36404891
- PMCID: PMC9668547
- DOI: 10.14309/crj.0000000000000905
Vedolizumab-Associated Hypereosinophilia and Hepatoxicity
Abstract
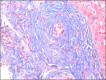
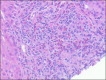
Vedolizumab, which is approved for the treatment of ulcerative colitis, has been associated with drug-induced liver injury because of an unclear mechanism. We describe the case of a 29-year-old man who presented with abnormal liver enzymes and peripheral hypereosinophilia after vedolizumab initiation. A complete workup for causes of hepatitis and hypereosinophilia was negative, and liver biopsy showed signs compatible with drug-induced liver injury. After the withdrawal of vedolizumab, the patient's eosinophil count and liver enzymes normalized. As vedolizumab becomes more prominent, it is important to understand the potential side-effect profile of vedolizumab.
© 2022 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of The American College of Gastroenterology.
Figures
References
-
- LiverTox. Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases: Bethesda, MD, 2012. - PubMed
-
- Vedolizumab (Entyvio) [package insert]. Takeda Pharamceuticals America: Deerfield, IL, 2014.
-
- Honap S, Sticova E, Theocharidou E, et al. . Vedolizumab-associated drug-induced liver injury: A case series. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2021;27(3):e32–e34. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials