Uncovering the Key Targets and Therapeutic Mechanisms of Qizhen Capsule in Gastric Cancer through Network Pharmacology and Bioinformatic Analyses
- PMID: 36404910
- PMCID: PMC9671734
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/1718143
Uncovering the Key Targets and Therapeutic Mechanisms of Qizhen Capsule in Gastric Cancer through Network Pharmacology and Bioinformatic Analyses
Abstract
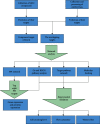
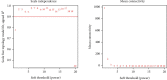
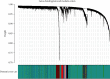
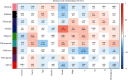
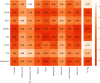
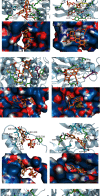
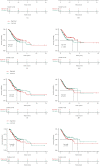
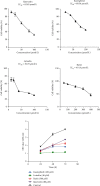
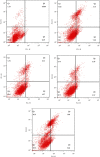
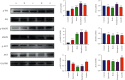
Objective. This study is aimed at screening out effective active compounds of Qizhen capsule (QZC) and exploring the underlying mechanisms against gastric cancer (GACA) by combining both bioinformatic analysis and experimental approaches. Weighted gene coexpression network analysis (WGCNA), network pharmacology, molecular docking simulation, survival analysis, and data-based differential gene and protein expression analysis were employed to predict QZC's potential targets and explore the underlying mechanisms. Subsequently, multiple experiments, including cell viability, apoptosis, and protein expression analyses, were conducted to validate the bioinformatics-predicted therapeutic targets. The results indicated that luteolin, rutin, quercetin, and kaempferol were vital active compounds, and TP53, MAPK1, and AKT1 were key targets. Molecular docking simulation showed that the four abovementioned active compounds had high binding affinities to the three main targets. Enrichment analysis showed that vital active compounds exerted therapeutic effects on GACA through regulating the TP53 pathway, MAPK pathway, and PI3K/AKT pathway. Furthermore, data-based gene expression analysis revealed that TP53 and JUN genes were not only differentially expressed between normal and GACA tissues but also correlated with clinical stages. In parallel, in vitro experimental results suggested that QZC exerted therapeutic effects on GACA by decreasing IC50 values, downregulating AKT expression, upregulating TP53 and MAPK expression, and increasing apoptosis of SGC-7901 cells. This study highlights the potential candidate biomarkers, therapeutic targets, and basic mechanisms of QZC in treating GACA, providing a foundation for new drug development, target mining, and related animal studies in GACA.
Copyright © 2022 Wanmei Zhou et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Elucidating the anti-aging mechanism of Si Jun Zi Tang by integrating network pharmacology and experimental validation in vivo.Aging (Albany NY). 2022 May 10;14(9):3941-3955. doi: 10.18632/aging.204055. Epub 2022 May 10. Aging (Albany NY). 2022. PMID: 35537009 Free PMC article.
-
Potential Molecular Mechanisms of Ephedra Herb in the Treatment of Nephrotic Syndrome Based on Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking.Biomed Res Int. 2022 Jul 5;2022:9214589. doi: 10.1155/2022/9214589. eCollection 2022. Biomed Res Int. 2022. PMID: 35837376 Free PMC article.
-
Network Pharmacology Prediction and Molecular Docking-Based Strategy to Discover the Potential Pharmacological Mechanism of Huai Hua San Against Ulcerative Colitis.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2021 Jul 28;15:3255-3276. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S319786. eCollection 2021. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2021. PMID: 34349502 Free PMC article.
-
Integrating Network Pharmacology and Experimental Verification to Explore the Pharmacological Mechanisms of Aloin Against Gastric Cancer.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2022 Jun 20;16:1947-1961. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S360790. eCollection 2022. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2022. PMID: 35757520 Free PMC article.
-
Erianin, the main active ingredient of Dendrobium chrysotoxum Lindl, inhibits precancerous lesions of gastric cancer (PLGC) through suppression of the HRAS-PI3K-AKT signaling pathway as revealed by network pharmacology and in vitro experimental verification.J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Oct 28;279:114399. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.114399. Epub 2021 Jul 8. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34246740
Cited by
-
Network Pharmacology, Molecular Docking, and Molecular Dynamic-Based Investigation on the Mechanism of Compound Chrysanthemum in the Treatment of Asthenopia.Comput Math Methods Med. 2022 Dec 30;2022:3444277. doi: 10.1155/2022/3444277. eCollection 2022. Comput Math Methods Med. 2022. PMID: 36619789 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Buonadonna A., Lombardi D., De A. P., Bidoli E., Frustaci S. Adenocarcinoma of the stomach: univariate and multivariate analyses of factors associated with survival. Journal of Ethnopharmacology . 2003;2(5):S31–S34. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

