Beneficial effects of CCL8 inhibition at lipopolysaccharide-induced lung injury
- PMID: 36404927
- PMCID: PMC9639378
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.105520
Beneficial effects of CCL8 inhibition at lipopolysaccharide-induced lung injury
Abstract
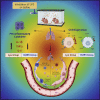
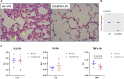
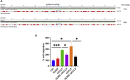
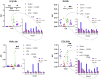
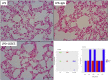
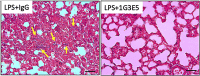
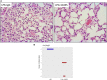
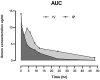
CCL8 (MCP-2) is a chemoattractive cytokine associated with various immune-related pathologies. Recent studies show that CCL8 is significantly stimulated during acute respiratory distress syndrome in severely ill patients with COVID-19, making the inhibition of CCL8 activity a promising treatment. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced lung injury was evaluated in mice using a neutralizing antibody (1G3E5) against human CCL8. Pharmacokinetic studies indicated that following IP administration, 1G3E5 was sustained at higher levels and for a longer period compared to IV administration. CCL8 expression in the lungs was not enhanced by LPS, but CCR2 and CCR5 receptors were significantly stimulated. 1G3E5-mediated inhibition of CCL8 was associated with the reduction of pulmonary inflammation and suppression of various pro-inflammatory cytokines. These results point to a previously unrecognized, permissive role for CCL8 in mediating cytokine induction and ultimately sustaining inflammation. Disruption of CCL8 activity may provide a strategy for mitigating pulmonary inflammation during lung injury when related to abnormal cytokine induction.
Keywords: Biological sciences; Immunology; Immunology specialty.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The University of South Carolina has filed patent applications for the 1G3E5 antibody. AN, EF, VK, IC, and HK are designated as inventors in these applications.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Synergistic up-regulation of MCP-2/CCL8 activity is counteracted by chemokine cleavage, limiting its inflammatory and anti-tumoral effects.Eur J Immunol. 2009 Mar;39(3):843-57. doi: 10.1002/eji.200838660. Eur J Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19224633
-
Cytokine and chemokine transcription profile during Mycoplasma pulmonis infection in susceptible and resistant strains of mice: macrophage inflammatory protein 1beta (CCL4) and monocyte chemoattractant protein 2 (CCL8) and accumulation of CCR5+ Th cells.Infect Immun. 2006 Oct;74(10):5943-54. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00082-06. Infect Immun. 2006. PMID: 16988274 Free PMC article.
-
Chemokine CCL8 and its receptor CCR5 in the spinal cord are involved in visceral pain induced by experimental colitis in mice.Brain Res Bull. 2017 Oct;135:170-178. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2017.10.009. Epub 2017 Oct 14. Brain Res Bull. 2017. PMID: 29037608
-
CCL8 enhances sensitivity of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma to photodynamic therapy by recruiting M1 macrophages.Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. 2019 Jun;26:235-243. doi: 10.1016/j.pdpdt.2019.03.014. Epub 2019 Mar 19. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. 2019. PMID: 30902794
-
FGF1 alleviates LPS-induced acute lung injury via suppression of inflammation and oxidative stress.Mol Med. 2022 Jun 28;28(1):73. doi: 10.1186/s10020-022-00502-8. Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 35764933 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Probiotic Bifidobacterium longum subsp. longum Protects against Cigarette Smoke-Induced Inflammation in Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 23;24(1):252. doi: 10.3390/ijms24010252. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36613693 Free PMC article.
-
Aggravated pneumonia and diabetes in SARS-CoV-2 infected diabetic mice.Emerg Microbes Infect. 2023 Dec;12(1):2203782. doi: 10.1080/22221751.2023.2203782. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2023. PMID: 37060137 Free PMC article.
-
Divergent Cytokine and Chemokine Responses at Early Acute Simian Immunodeficiency Virus Infection Correlated with Virus Replication and CD4 T Cell Loss in a Rhesus Macaque Model.Vaccines (Basel). 2023 Jan 25;11(2):264. doi: 10.3390/vaccines11020264. Vaccines (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36851142 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring common biomarkers of ischemic stroke and obstructive sleep apnea through bioinformatics analysis.PLoS One. 2024 Oct 30;19(10):e0312013. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0312013. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39475897 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxic niches attract and sequester tumor-associated macrophages and cytotoxic T cells and reprogram them for immunosuppression.Immunity. 2023 Aug 8;56(8):1825-1843.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2023.06.017. Epub 2023 Jul 13. Immunity. 2023. PMID: 37451265 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

