Identification of potential inhibitors of brain-specific CYP46A1 from phytoconstituents in Indian traditional medicinal plants
- PMID: 36404953
- PMCID: PMC9667835
- DOI: 10.1007/s42485-022-00098-x
Identification of potential inhibitors of brain-specific CYP46A1 from phytoconstituents in Indian traditional medicinal plants
Abstract
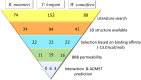
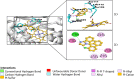
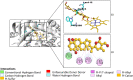
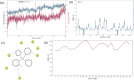
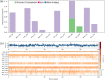
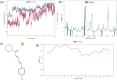
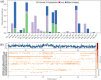
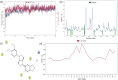
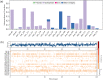
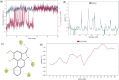
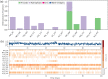
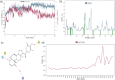
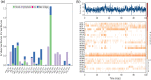
Cytochrome P450 46A1 (CYP46A1) is a crucial enzyme in brain that converts cholesterol to 24 (S) hydroxy cholesterol thereby increasing its polarity to facilitate removal of excess cholesterol from the CNS. The inhibition of CYP46A1 with several synthetic molecules has been investigated extensively for treatment of Alzheimer's disease, Huntington's disease, glaucoma, and in hippocampal neurons from aged mice. However, phytochemicals have received far little attention in studies involving development of potential CYP46A1 inhibitors. Thus, in the present study phytoconstituents from Indian traditional medicinal plants; Bacopa monnieri, Piper longum, and Withania somnifera, were virtually screened for interaction with CYP46A1 using computational tools. Out of three plants, six molecules from P. longum and three molecules from W. somnifera were shortlisted to study interactions with CYP46A1 based on the physio-chemical parameters. Fargesin, piperolactam A and coumaperine from P. longum showed the higher binding affinity and the values were - 10.3, - 9.5, - 9.0 kcal/moles respectively, whereas, withaferin A from W. somnifera had a binding affinity of - 12.9 kcal/mol. These were selected as potential modulators as they exhibited suitable interactions with active site residues; Tyr109, Leu112, Trp368, Gly369, and Ala474. The selected molecules were further subjected to molecular dynamics simulation. Further, the pharmacological properties of molecules were also predicted using ADMET calculator and the data revealed that all the selected compounds had good absorption as well as solubility characteristics. In addition, sesamin, fargesin, piperolactam A, and coumaperine had minimal or no toxic effects. Thus, the study successfully identified compounds from Indian medicinal plants that may serve as potential inhibitors of CYP46A1 or base structures to design novel CYP46A1 inhibitors, which may be effective in treating neurological conditions involving perturbed cholesterol homeostasis.
Supplementary information: The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1007/s42485-022-00098-x.
Keywords: Brain; Cholesterol; Cytochrome P450; In Silico; Lipids; Phytochemicals.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd. 2022, Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestAuthors do not have any conflict of interest.
Figures
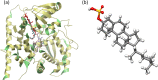

References
-
- Azizidoost S, Babaahmadi-Rezaei H, Nazeri Z, Cheraghzadeh M, Kheirollah A. Amyloid beta increases ABCA1 and HMGCR protein expression, and cholesterol synthesis and accumulation in mice neurons and astrocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2022;1867(1):159069. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2021.159069. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
