Factors associated with diabetic retinopathy screening and regular eye checkup practice among diabetic patients attending Felege Hiwot Specialized Hospital
- PMID: 36404973
- PMCID: PMC9631195
- DOI: 10.18240/ijo.2022.11.14
Factors associated with diabetic retinopathy screening and regular eye checkup practice among diabetic patients attending Felege Hiwot Specialized Hospital
Abstract
Aim: To identify associated factors of diabetic retinopathy (DR) screening and ey e check-up practice among diabetes mellitus (DM) patients attending Felege Hiwot Specialized Hospital.
Methods: An institution-based cross-sectional study was applied from October 4, 2019 to January 12, 2020 at Felege Hiwot Specialized Hospital. A systematic random sampling technique was used to recruit participants and an interviewer-administered questionnaire was employed to collect the data. The collected data were entered into Epi Info version 7 and transposed to SPSS version 24 for statistical analysis. Descriptive statistics were executed and associated factors were identified using binary logistic regression. The strength of association between the independent and the outcome variable was determined using an adjusted odds ratio (AOR) with 95% confidence interval (CI).
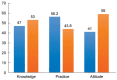
Results: Four hundred and six participants partake with a response rate of 95.7% and a mean age of 47±11.5y. The magnitude of DR screening was 308 (75.9%, 95%CI: 71.5%, 79.8%). Higher educational level (AOR=3.25; 95%CI: 1.40, 8.78), good knowledge of DR (AOR=2.50; 95%CI: 1.55, 4.46), and family history of DM (AOR=2.15; 95%CI: 1.41, 3.85) were significantly associated with DR screening. On the other side, rural residence [AOR=3.11 (1.89, 5.02)] and undesirable attitudes toward DR [AOR=5.65 (3.14, 8.76)] were significantly associated with poor regular eye checkup practice.
Conclusion: Most of the participants are screened for DR. Higher education, family history, and good knowledge are associated with DR screening. In addition, rural residence and undesirable attitudes toward DR are associated with regular eye checkup practice.
Keywords: Ethiopia; diabetes mellitus; diabetic retinopathy; eye checkup; eye screening.
International Journal of Ophthalmology Press.
Figures
References
-
- Flaxel CJ, Adelman RA, Bailey ST, Fawzi A, Lim JI, Vemulakonda GA, Ying GS. Posterior vitreous detachment, retinal breaks, and lattice degeneration preferred practice pattern®. Ophthalmology. 2020;127(1):P146–P181. - PubMed
-
- Park YS, Heo H, Ye BJ, Suh YW, Kim SH, Park SH, Lim KH, Lee SJ, Park SH, Baek SH, Epidemiologic Survey Committee of the Korean Ophthalmological Society Prevalence and factors associated with the use of eye care services in south Korea: Korea national health and nutrition examination survey 2010-2012. Korean J Ophthalmol. 2017;31(1):58–70. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Islam FMA, Kawasaki R, Finger RP. Factors associated with participation in a diabetic retinopathy screening program in a rural district in Bangladesh. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2018;144:111–117. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources