Epidemiology of liver cirrhosis and associated complications: Current knowledge and future directions
- PMID: 36405106
- PMCID: PMC9669831
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i41.5910
Epidemiology of liver cirrhosis and associated complications: Current knowledge and future directions
Abstract
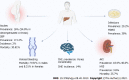
Cirrhosis causes a heavy global burden. In this review, we summarized up-to-date epidemiological features of cirrhosis and its complications. Recent epidemiological studies reported an increase in the prevalence of cirrhosis in 2017 compared to in 1990 in both men and women, with 5.2 million cases of cirrhosis and chronic liver disease occurring in 2017. Cirrhosis caused 1.48 million deaths in 2019, an increase of 8.1% compared to 2017. Disability-adjusted life-years due to cirrhosis ranked 16th among all diseases and 7th in people aged 50-74 years in 2019. The global burden of hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus-associated cirrhosis is decreasing, while the burden of cirrhosis due to alcohol and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is increasing rapidly. We described the current epidemiology of the major complications of cirrhosis, including ascites, variceal bleeding, hepatic encephalopathy, renal disorders, and infections. We also summarized the epidemiology of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with cirrhosis. In the future, NAFLD-related cirrhosis will likely become more common due to the prevalence of metabolic diseases such as obesity and diabetes, and the prevalence of alcohol-induced cirrhosis is increasing. This altered epidemiology should be clinically noted, and relevant interventions should be undertaken.
Keywords: Burden; Causes; Cirrhosis; Complications; Cost; Epidemiology; Feature.
©The Author(s) 2022. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors declare no conflict of interest in this study.
Figures
References
-
- Kisseleva T, Brenner D. Molecular and cellular mechanisms of liver fibrosis and its regression. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;18:151–166. - PubMed
-
- Campana L, Esser H, Huch M, Forbes S. Liver regeneration and inflammation: from fundamental science to clinical applications. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2021;22:608–624. - PubMed
-
- D'Amico G, Morabito A, D'Amico M, Pasta L, Malizia G, Rebora P, Valsecchi MG. Clinical states of cirrhosis and competing risks. J Hepatol. 2018;68:563–576. - PubMed
-
- Ginès P, Krag A, Abraldes JG, Solà E, Fabrellas N, Kamath PS. Liver cirrhosis. Lancet. 2021;398:1359–1376. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

