Experience with enteral sulfonylurea monotherapy for extremely low birth weight infants with hyperglycemia
- PMID: 36405438
- PMCID: PMC9637416
- DOI: 10.1297/cpe.2022-0018
Experience with enteral sulfonylurea monotherapy for extremely low birth weight infants with hyperglycemia
Abstract
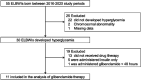
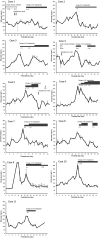
Limited data are available on the effects of enteral sulfonylurea (SU) monotherapy in extremely low birth weight infants (ELBWIs) with hyperglycemia. Therefore, we report our experience with enteral SU monotherapy for hyperglycemic ELBWIs. We retrospectively evaluated 11 hyperglycemic ELBWIs (seven male infants, median gestational age = 24.9 wk) who received SU between January 2016 and December 2019. Blood glucose (BG) levels were monitored before and after SU initiation and evaluated for the occurrence of adverse effects. We administered SU at a median of 15 d (interquartile range [IQR]: 12-20 d) after birth, with the median maximum dose of 0.2 mg/kg/d (IQR: 0.125-0.3 mg/kg/d). Hyperglycemia improved in all patients, and the target BG levels were achieved without severe side effects at a median of 6 d (IQR: 4-8.5 d) after initiation of treatment. The incidence of hypoglycemia during SU treatment was observed in 18 events per 1000 patient hours; however, the patients were asymptomatic. Based on these results, enteral SU monotherapy may be considered as an option for hyperglycemic ELBWIs.
Keywords: extremely low birth weight; glyburide (glibenclamide); hyperglycemia; infant; sulfonylurea.
2022©The Japanese Society for Pediatric Endocrinology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prematurity at less than 24 weeks of gestation is a risk for prolonged hyperglycemia in extremely low-birth weight infants.Endocrine. 2020 Oct;70(1):71-77. doi: 10.1007/s12020-020-02393-3. Epub 2020 Jul 2. Endocrine. 2020. PMID: 32617755
-
Risk factors for hyperglycemia in extremely low birth weight infants during the first 14 days.Pediatr Neonatol. 2022 Jan;63(1):13-18. doi: 10.1016/j.pedneo.2021.07.001. Epub 2021 Jul 17. Pediatr Neonatol. 2022. PMID: 34330686
-
Outcomes of early nutrition support in extremely low-birth-weight infants.Nutr Clin Pract. 2006 Aug;21(4):395-400. doi: 10.1177/0115426506021004395. Nutr Clin Pract. 2006. PMID: 16870808
-
Hyperglycemia in Extremely Preterm Infants.Neoreviews. 2020 Feb;21(2):e89-e97. doi: 10.1542/neo.21-2-e89. Neoreviews. 2020. PMID: 32005719 Review.
-
Non-severe Hypoglycemia Risk Difference between Sulfonylurea and Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors (SGLT2-I) as an Add-On to Metformin in Randomized Controlled Trials.J Popul Ther Clin Pharmacol. 2017 May 23;24(2):e32-e40. doi: 10.22374/1710-6222.24.2.6. J Popul Ther Clin Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28594482 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
