The Induction of Hypothyroidism during Gestation Decreases Outer Hair Cell Motility in Rat Offspring
- PMID: 36405453
- PMCID: PMC9668424
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0042-1745856
The Induction of Hypothyroidism during Gestation Decreases Outer Hair Cell Motility in Rat Offspring
Abstract
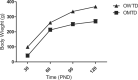
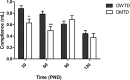
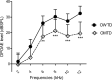
Introduction Perinatal hypothyroidism has a negative repercussion on the development and maturation of auditory system function. However, its long-term effect on auditory function remains unsettled. Objective To evaluate the effect of prenatal hypothyroidism on the auditory function of adult offspring in rats. Methods Pregnant Wistar rats were given the antithyroid drug methimazole (0.02% -1-methylimidazole-2-thiol- MMI) in drinking water, ad libitum, from gestational day (GD) 9 to postnatal day 15 (PND15). Anesthetized offspring from MMI-treated dams (OMTD) and control rats were evaluated by tympanometry, distortion product otoacoustic emission (DPOAE), and auditory brainstem response (ABR) at PNDs 30, 60, 90, and 120. Results Our data demonstrated no middle ear dysfunction, with the OMTD compliance lower than that of the control group. The DPOAE revealed the absence of outer hair cells function, and the ABR showed normal integrity of neural auditory pathways up to brainstem level in the central nervous system. Furthermore, in the OMTD group, hearing loss was characterized by a higher electrophysiological threshold. Conclusion Our data suggest that perinatal hypothyroidism leads to irreversible damage to cochlear function in offspring.
Keywords: cochlea; congenital hypothyroidism; hearing loss.
Fundação Otorrinolaringologia. This is an open access article published by Thieme under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonDerivative-NonCommercial License, permitting copying and reproduction so long as the original work is given appropriate credit. Contents may not be used for commecial purposes, or adapted, remixed, transformed or built upon. ( https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/ ).
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interests The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests.
Figures
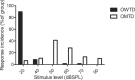
References
-
- Davis J M, Elfenbein J, Schum R, Bentler R A. Effects of mild and moderate hearing impairments on language, educational, and psychosocial behavior of children. J Speech Hear Disord. 1986;51(01):53–62. - PubMed
-
- Wada H, Yumoto S, Iso H. Irreversible damage to auditory system functions caused by perinatal hypothyroidism in rats. Neurotoxicol Teratol. 2013;37:18–22. - PubMed
-
- Eastman C J. Screening for thyroid disease and iodine deficiency. Pathology. 2012;44(02):153–159. - PubMed
-
- Lazarus J, Brown R S, Daumerie C, Hubalewska-Dydejczyk A, Negro R, Vaidya B.2014 European thyroid association guidelines for the management of subclinical hypothyroidism in pregnancy and in children Eur Thyroid J 201430276–94.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25114871[Internet] - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

