The effects of selenium supplementation on inflammatory markers in critically ill patients
- PMID: 36405547
- PMCID: PMC9643959
- DOI: 10.1007/s42452-022-05208-4
The effects of selenium supplementation on inflammatory markers in critically ill patients
Abstract
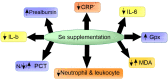
Abstract: Low serum selenium (Se) levels have been shown in critical illness, which is associated with poor clinical outcomes and a higher mortality rate. Se plays an important role in inflammation and oxidative stress. Since the overproduction of inflammatory cytokines and increased oxidative stress is a major component of critical illnesses, its supplementation has been demonstrated to have promising effects on critically ill patients. This study aims to review the evidence regarding the effects of Se supplementation on inflammatory and oxidative markers in critically ill patients. The literature review highlights alterations of inflammatory markers, including procalcitonin, leukocyte count, albumin, prealbumin, C-reactive protein (CRP), inflammatory cytokines, and cholesterol following Se supplementation in critically ill patients. Besides, the antioxidant properties of Se due to its presence in the structure of several selenoenzymes have been reported.
Article highlights: Low serum Se level have been shown in critical illness, which is associated with poor clinical outcome and higher mortality rate.Se plays an important role in inflammation and oxidative stress.Se supplementation can have promising effects by alterations of inflammatory markers and its antioxidant properties for critically ill patients.
Keywords: Critical illness; Inflammation; Oxidative stress; Selenium; Supplemtation.
© The Author(s) 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Di Leo I et al. (2016) Organoselenium compounds, an overview on the biological activities beyond antioxidant properties. In: Proceedings of the 20th international electronic conference on synthetic organic chemistry (ECSOC)
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous