Feasibility of artificial-intelligence-based synthetic computed tomography in a magnetic resonance-only radiotherapy workflow for brain radiotherapy: Two-way dose validation and 2D/2D kV-image-based positioning
- PMID: 36405564
- PMCID: PMC9667284
- DOI: 10.1016/j.phro.2022.10.002
Feasibility of artificial-intelligence-based synthetic computed tomography in a magnetic resonance-only radiotherapy workflow for brain radiotherapy: Two-way dose validation and 2D/2D kV-image-based positioning
Abstract
Background and purpose: Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)-only workflow eliminates the MRI-computed tomography (CT) registration inaccuracy, which degrades radiotherapy (RT) treatment accuracy. For an MRI-only workflow MRI sequences need to be converted to synthetic-CT (sCT). The purpose of this study was to evaluate a commercially available artificial intelligence (AI)-based sCT generation for dose calculation and 2D/2D kV-image daily positioning for brain RT workflow.
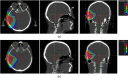
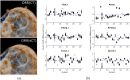
Materials and methods: T1-VIBE DIXON was acquired at the 1.5 T MRI for 26 patients in RT setup for sCTs generation. For each patient, a volumetric modulated arc therapy (VMAT) plan was optimized on the CT, then recalculated on the sCT; and vice versa. sCT-based digitally reconstructed radiographs (DRRs) were fused with stereoscopic X-ray images recorded as image guidance for clinical treatments. Dosimetric differences between planned/recalculated doses and the differences between the calculated and recorded clinical couch shift/rotation were evaluated.
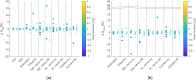
Results: Mean ΔD50 between planned/recalculated doses for target volumes ranged between -0.2 % and 0.2 %; mean ΔD50 and ΔD0.01ccm were -0.6 % and 1.6 % and -1.4 % and 1.0 % for organ-at-risks, respectively. Differences were tested for clinical equivalence using intervals ±2 % (dose), ±1mm (translation), and ±1° (rotation). Dose equivalence was found using ±2 % interval (p < 0.001). The median differences between lat./long./vert. couch shift between CT-based/sCT-based DRRs were 0.3 mm/0.2 mm/0.3 mm (p < 0.05); median differences between lat./long./vert. couch rotation were -1.5°/0.1°/0.1° (after improvement of RT setup: -0.4°/-0.1°/-0.4°, p < 0.05).
Conclusions: This in-silico study showed that the AI-based sCT provided equivalent results to the CT for dose calculation and daily stereoscopic X-ray positioning when using an optimal RT setup during MRI acquisition.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence; Brain radiotherapy; MRI-only workflow; Synthetic CT; kV-image-based positioning.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

