Electroencephalography spectral edge frequency and suppression rate-guided sedation in patients with COVID-19: A randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 36405604
- PMCID: PMC9671936
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2022.1013430
Electroencephalography spectral edge frequency and suppression rate-guided sedation in patients with COVID-19: A randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Sedation in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients has been identified as a major challenge. We aimed to investigate whether the use of a multiparameter electroencephalogram (EEG) protocol to guide sedation in COVID-19 patients would increase the 30-day mechanical ventilation-free days (VFD).
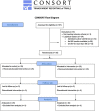
Methods: We conducted a double-blind randomized clinical trial. We included patients with severe pneumonia due to COVID-19 who required mechanical ventilation (MV) and deep sedation. We randomized to the control (n = 25) or multiparameter group (n = 25). Sedation in the intervention group was administered following the standard institutional protocols together with a flow chart designed to reduce the propofol administration dose if the EEG suppression rate was over 2% or the spectral edge frequency 95 (SEF95) was below 10 Hz. We performed an intention-to-treat analysis to evaluate our primary outcome (30-day VFD).
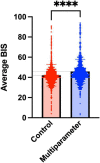
Results: There was no difference in VFD at day 30 (median: 11 [IQR 0-20] days in the control group vs. 0 [IQR 0-21] days in the BIS multiparameter group, p = 0.87). Among secondary outcomes, we documented a 17% reduction in the total adjusted propofol administered during the first 5 days of the protocol [median: 2.3 (IQR 1.9-2.8) mg/k/h in the control group vs. 1.9(IQR 1.5-2.2) mg/k/h in the MP group, p = 0.005]. This was accompanied by a higher average BIS value in the intervention group throughout the treatment period.
Conclusion: A sedation protocol guided by multivariate EEG-derived parameters did not increase the 30-day VFD. However, the intervention led to a reduction in total propofol administration.
Keywords: COVID-19; bispectral index; electroencephalogram; sedation; spectral edge frequency; suppression rate.
Copyright © 2022 Tobar, Farías, Rojas, Penna, Egaña, Ponce, Bravo, Maldonado, Gajardo and Gutiérrez.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

