Roles and crosstalks of macrophages in diabetic nephropathy
- PMID: 36405700
- PMCID: PMC9666695
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1015142
Roles and crosstalks of macrophages in diabetic nephropathy
Abstract
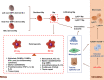
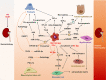
Diabetic nephropathy (DN) is the most common chronic kidney disease. Accumulation of glucose and metabolites activates resident macrophages in kidneys. Resident macrophages play diverse roles on diabetic kidney injuries by releasing cytokines/chemokines, recruiting peripheral monocytes/macrophages, enhancing renal cell injuries (podocytes, mesangial cells, endothelial cells and tubular epithelial cells), and macrophage-myofibroblast transition. The differentiation and cross-talks of macrophages ultimately result renal inflammation and fibrosis in DN. Emerging evidence shows that targeting macrophages by suppressing macrophage activation/transition, and macrophages-cell interactions may be a promising approach to attenuate DN. In the review, we summarized the diverse roles of macrophages and the cross-talks to other cells in DN, and highlighted the therapeutic potentials by targeting macrophages.
Keywords: diabetic nephropathy; fibrosis; inflammation; macrophage; metabolic disorder.
Copyright © 2022 Li, You, Shao, Wu, Wang, Guo, Meng and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Fox CS, Matsushita K, Woodward M, Bilo HJ, Chalmers J, Heerspink HJ, et al. . Associations of kidney disease measures with mortality and end-stage renal disease in individuals with and without diabetes: a meta-analysis. Lancet (2012) 380(9854):1662–73. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61350-6 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

