From bench to bedside: Calprotectin (S100A8/S100A9) as a biomarker in rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 36405711
- PMCID: PMC9672845
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1001025
From bench to bedside: Calprotectin (S100A8/S100A9) as a biomarker in rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
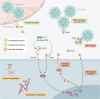
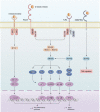
S100A9/S100A8 (calprotectin), a member of the S100 protein family, has been shown to play a pivotal role in innate immunity activation. Calprotectin plays a critical role in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis (RA), as it triggers chemotaxis, phagocyte migration and modulation of neutrophils and macrophages. Higher calprotectin levels have been found in synovial fluid, plasma, and serum from RA patients. Recent studies have demonstrated better correlations between serum or plasma calprotectin and composite inflammatory disease activity indexes than c-reactive protein (CRP) or the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR). Calprotectin serum levels decreased after treatment, independently of the DMARD type or strategy. Calprotectin has shown the strongest correlations with other sensitive techniques to detect inflammation, such as ultrasound. Calprotectin independently predicts radiographic progression. However, its value as a biomarker of treatment response and flare after tapering is unclear. This update reviews the current understanding of calprotectin in RA and discusses possible applications as a biomarker in clinical practice.
Keywords: CRP - C-reactive protein; acute phase reactants; biomarker; calprotectin; rheumatoid arthritis.
Copyright © 2022 Inciarte-Mundo, Frade-Sosa and Sanmartí.
Conflict of interest statement
JI-M has received honoraria from AbbVie employee. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Calprotectin (S100A8/S100A9) detects inflammatory activity in rheumatoid arthritis patients receiving tocilizumab therapy.Arthritis Res Ther. 2022 Aug 19;24(1):200. doi: 10.1186/s13075-022-02887-7. Arthritis Res Ther. 2022. PMID: 35986420 Free PMC article.
-
Calprotectin (S100A8/A9) and S100A12 are associated with measures of disease activity in a longitudinal study of patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with infliximab.Scand J Rheumatol. 2016 Jul;45(4):274-81. doi: 10.3109/03009742.2015.1107128. Epub 2016 Jan 15. Scand J Rheumatol. 2016. PMID: 26767827 Clinical Trial.
-
Calprotectin, a sensitive marker of inflammation, is robustly assessed in plasma from patients with early or established rheumatoid arthritis by use of different laboratory methods.Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 2023 Sep;83(5):330-335. doi: 10.1080/00365513.2023.2225223. Epub 2023 Jun 21. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 2023. PMID: 37343245
-
S100A8/A9 as a biomarker for synovial inflammation and joint damage in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.Korean J Intern Med. 2014 Jan;29(1):12-9. doi: 10.3904/kjim.2014.29.1.12. Epub 2014 Jan 2. Korean J Intern Med. 2014. PMID: 24574827 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Calprotectin in Rheumatoid Arthritis.J Transl Int Med. 2019 Dec 31;7(4):126-131. doi: 10.2478/jtim-2019-0026. eCollection 2019 Dec. J Transl Int Med. 2019. PMID: 32010597 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of DiaSorin Liaison® calprotectin fecal assay adapted for pleural effusion.Adv Lab Med. 2023 Nov 14;4(4):419-424. doi: 10.1515/almed-2023-0106. eCollection 2023 Dec. Adv Lab Med. 2023. PMID: 38106502 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the prognostic nutritional index (PNI) as a tool for assessing disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis patients.Clin Rheumatol. 2024 May;43(5):1461-1467. doi: 10.1007/s10067-024-06927-2. Epub 2024 Mar 11. Clin Rheumatol. 2024. PMID: 38466500
-
Prognostic value of serum Mrp 8/14 in sepsis-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome patients: a retrospective cohort study.PeerJ. 2024 Dec 13;12:e18718. doi: 10.7717/peerj.18718. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 39686985 Free PMC article.
-
Serum calprotectin correlates with severity of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome.Front Microbiol. 2025 Jun 27;16:1604243. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1604243. eCollection 2025. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40657502 Free PMC article.
-
Association of maternal calprotectin plasma levels with abruption placenta.BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2025 Mar 7;25(1):249. doi: 10.1186/s12884-025-07356-y. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2025. PMID: 40055628 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ryckman C, McColl SR, Vandal K, de Médicis R, Lussier A, Poubelle PE, et al. . Role of S100A8 and S100A9 in neutrophil recruitment in response to monosodium urate monohydrate crystals in the air-pouch model of acute gouty arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol (2003) 48(8):2310–20. doi: 10.1002/art.11079 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

