Tumor-derived extracellular vesicles modulate innate immune responses to affect tumor progression
- PMID: 36405712
- PMCID: PMC9667034
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1045624
Tumor-derived extracellular vesicles modulate innate immune responses to affect tumor progression
Abstract
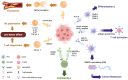
Immune cells are capable of influencing tumor progression in the tumor microenvironment (TME). Meanwhile, one mechanism by which tumor modulate immune cells function is through extracellular vesicles (EVs), which are cell-derived extracellular membrane vesicles. EVs can act as mediators of intercellular communication and can deliver nucleic acids, proteins, lipids, and other signaling molecules between cells. In recent years, studies have found that EVs play a crucial role in the communication between tumor cells and immune cells. Innate immunity is the first-line response of the immune system against tumor progression. Therefore, tumor cell-derived EVs (TDEVs) which modulate the functional change of innate immune cells serve important functions in the context of tumor progression. Emerging evidence has shown that TDEVs dually enhance or suppress innate immunity through various pathways. This review aims to summarize the influence of TDEVs on macrophages, dendritic cells, neutrophils, and natural killer cells. We also summarize their further effects on the progression of tumors, which may provide new ideas for developing novel tumor therapies targeting EVs.
Keywords: dendritic cells; macrophages; natural killer cells; neutrophils; tumor progression; tumor-derived extracellular vesicles (TDEVs).
Copyright © 2022 Wang, Sun, Dastgheyb and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Thery C, Witwer KW, Aikawa E, Alcaraz MJ, Anderson JD, Andriantsitohaina R, et al. . Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (Misev2018): A position statement of the international society for extracellular vesicles and update of the Misev2014 guidelines. J Extracell Vesicles (2018) 7(1):1535750. doi: 10.1080/20013078.2018.1535750 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

