Interleukin-6 and indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase as potential adjuvant targets for Papillomavirus-related tumors immunotherapy
- PMID: 36405719
- PMCID: PMC9668887
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1005937
Interleukin-6 and indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase as potential adjuvant targets for Papillomavirus-related tumors immunotherapy
Abstract
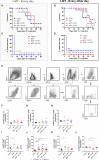
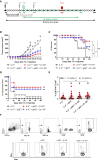
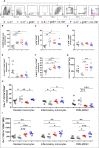
High-risk Human papillomavirus (HPV) infections represent an important public health issue. Nearly all cervical malignancies are associated with HPV, and a range of other female and male cancers, such as anogenital and oropharyngeal. Aiming to treat HPV-related tumors, our group developed vaccines based on the genetic fusion of the HSV-1 glycoprotein D (gD) with the HPV-16 E7 oncoprotein (gDE7 vaccines). Despite the promising antitumor results reached by gDE7 vaccines in mice, combined therapies may increase the therapeutic effects by improving antitumor responses and halting immune suppressive mechanisms elicited by tumor cells. Considering cancer immunosuppressive mechanisms, indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) enzyme and interleukin-6 (IL-6) stand out in HPV-related tumors. Since IL-6 sustained the constitutive IDO expression, here we evaluated the therapeutic outcomes achieved by the combination of active immunotherapy based on a gDE7 protein-based vaccine with adjuvant treatments involving blocking IDO, either by use of IDO inhibitors or IL-6 knockout mice. C57BL/6 wild-type (WT) and transgenic IL-6-/- mice were engrafted with HPV16-E6/E7-expressing TC-1 cells and treated with 1-methyl-tryptophan isoforms (D-1MT and DL-1MT), capable to inhibit IDO. In vitro, the 1MT isoforms reduced IL-6 gene expression and IL-6 secretion in TC-1 cells. In vivo, the multi-targeted treatment improved the antitumor efficacy of the gDE7-based protein vaccine. Although the gDE7 immunization achieves partial tumor mass control in combination with D-1MT or DL-1MT in WT mice or when administered in IL-6-/- mice, the combination of gDE7 and 1MT in IL-6-/- mice further enhanced the antitumor effects, reaching total tumor rejection. The outcome of the combined therapy was associated with an increased frequency of activated dendritic cells and decreased frequencies of intratumoral polymorphonuclear myeloid-derived suppressor cells and T regulatory cells. In conclusion, the present study demonstrated that IL-6 and IDO negatively contribute to the activation of immune cells, particularly dendritic cells, reducing gDE7 vaccine-induced protective immune responses and, therefore, opening perspectives for the use of combined strategies based on inhibition of IL-6 and IDO as immunometabolic adjuvants for immunotherapies against HPV-related tumors.
Keywords: HPV; IDO; IL-6; cancer; immunotherapy; vaccine.
Copyright © 2022 Pagni, Souza, Pegoraro, Porchia, da Silva, Aps, Silva, Rodrigues, Sales, Ferreira and Moreno.
Conflict of interest statement
BP and LA hold ownership interest, including patents, in ImunoTera Soluções Terapêuticas Ltda. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The Combined Use of Melatonin and an Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase-1 Inhibitor Enhances Vaccine-Induced Protective Cellular Immunity to HPV16-Associated Tumors.Front Immunol. 2018 Aug 22;9:1914. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01914. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30186285 Free PMC article.
-
Herpes Simplex Virus Glycoprotein D Targets a Specific Dendritic Cell Subset and Improves the Performance of Vaccines to Human Papillomavirus-Associated Tumors.Mol Cancer Ther. 2017 Sep;16(9):1922-1933. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-17-0071. Epub 2017 May 18. Mol Cancer Ther. 2017. PMID: 28522585
-
Expression of a soluble IL-10 receptor enhances the therapeutic effects of a papillomavirus-associated antitumor vaccine in a murine model.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2019 May;68(5):753-763. doi: 10.1007/s00262-018-02297-2. Epub 2019 Feb 26. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2019. PMID: 30806747 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic gene modified cell based cancer vaccines.Gene. 2013 Aug 10;525(2):200-7. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2013.03.056. Epub 2013 Apr 6. Gene. 2013. PMID: 23566846 Review.
-
Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase: is it an immune suppressor?Cancer J. 2010 Jul-Aug;16(4):354-9. doi: 10.1097/PPO.0b013e3181eb3343. Cancer J. 2010. PMID: 20693847 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Role of indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase 1 in modulating the malignant biological behavior of cervical cancer cells through the Tryptophan-Kynurenine pathway.J Mol Histol. 2025 Aug 22;56(5):276. doi: 10.1007/s10735-025-10570-9. J Mol Histol. 2025. PMID: 40844661
-
Plasticity of myeloid-derived suppressor cells in cancer and cancer therapy.Oncol Res. 2025 Jun 26;33(7):1581-1592. doi: 10.32604/or.2025.060063. eCollection 2025. Oncol Res. 2025. PMID: 40612857 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Revolutionizing adjuvant development: harnessing AI for next-generation cancer vaccines.Front Immunol. 2024 Aug 14;15:1438030. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1438030. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39206192 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combined Inhibition of Indolamine-2,3-Dioxygenase 1 and C-X-C Chemokine Receptor Type 2 Exerts Antitumor Effects in a Preclinical Model of Cervical Cancer.Biomedicines. 2023 Aug 16;11(8):2280. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11082280. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37626777 Free PMC article.
-
HPV infection and the immune microenvironment in cervical cancer.Front Immunol. 2025 Jul 30;16:1645019. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1645019. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40808954 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Signorini Filho RC, Colturato LF, Barbosa GB, Rosa TSF, Gebrim LH. Clinical and histopathological comparison of two historical series of 142 wertheim-meigs operations performed in a reference center in Brazil. Int J Women’s Heal Wellness (2017) 3:55. doi: 10.23937/2474-1353/1510055 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

